Cables and Connectivity: Ultimate 2025 Guide
The Unseen Pathways: Decoding Cables and Connectivity
The Foundation: Why Physical Cables Still Reign Supreme
Think of networking cables as the quiet, hard-working heroes of our digital world. While Wi-Fi offers amazing freedom and convenience, cables and connectivity are where the true muscle lies. For businesses and demanding tasks, wired networks consistently deliver top-notch signal strength, rock-solid reliability, and essential security. Trying to run a busy office or a data center on Wi-Fi alone? It would be like driving on a bumpy, crowded road instead of a smooth, dedicated highway! Wired connections are simply critical for smooth operations.
Wired vs. Wireless Networks: A Head-to-Head Comparison
When it comes to building a network, you’ll often hear about wired versus wireless options. Both have their place, but for the truly important stuff, wired connections almost always come out on top.
- Speed and Performance: Imagine a dedicated lane just for your data. That’s what wired networks offer. They provide incredible speeds and bandwidth. For example, a good Ethernet cable can easily handle speeds up to 10 Gigabits per second (Gbps). Wireless speeds, while much better than before, are often shared among many devices. They can also slow down a lot based on how far away you are, what’s in the way, and how many other Wi-Fi signals are around.
- Latency (Digital Lag): This is how long it takes for information to travel from one point to another. Wired connections have super low latency. This is a big deal for things like clear phone calls (Voice over IP or VoIP) and smooth video meetings. Even tiny delays can make a big difference here.
- Interference: Wireless signals can get messed up by other electronic gadgets like microwaves, cordless phones, or even your neighbor’s Wi-Fi. It’s like trying to have a conversation in a noisy room. Wired connections, especially shielded ones, are much more protected from this “digital noise.” That’s why Ethernet cables have those twisted pairs of wires – it helps cancel out interference!
- Reliability: Once a cable is properly set up, it provides a very stable and dedicated pathway for your data. Wireless signals, on the other hand, can be blocked by walls and floors, get weaker over distance, and slow down when too many devices are trying to connect at once. Wired connections are simply more dependable day in and day out.
- Security: While no network is perfectly safe, wired networks offer a higher level of physical security. To get into a wired network, someone usually needs to physically plug in or access a device. Wireless networks, because they send signals through the air, can be easier to intercept if they’re not properly secured with strong encryption.
For all these reasons, businesses overwhelmingly choose wired infrastructure for their most important tasks. It just ensures your data is handled consistently and reliably.
The Role of Cables in Modern Infrastructure
The unseen network of cables and connectivity is the very foundation of nearly everything we do digitally. From handling global money transactions to streaming your favorite movie, cables play an absolutely vital role.
- Data Centers: These are like the massive brains of our digital world, holding huge amounts of information. Inside them, cables are everything. Ethernet and fiber optic cables act as the super-fast highways that move data between servers, storage devices, and all the other critical gear. We’re talking about connections that need to be incredibly fast and reliable, with almost no lag time.
- Business Phone Systems: Modern business phones, especially those using Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), rely heavily on strong network cabling. A cool feature called Power over Ethernet (PoE) often makes things easier by sending both data and power over a single Ethernet cable. This makes setting up VoIP phones super efficient.
- Industrial Automation: In factories and industrial settings, machines “talk” to each other and to control systems. Here, reliable cables and connectivity are not just important, they’re essential. These environments often need special, tough cables that can handle harsh conditions, making sure everything runs smoothly and safely.
- Home Theaters: For the very best picture and sound, many home theater fans choose wired connections. For example, fiber optic cables are excellent for connecting devices because they can send high-quality digital signals without any loss.
- Global Connectivity: While we often think about our local networks, the internet itself is a giant network of networks. And guess what connects them all? Massive underwater fiber optic cables! These amazing submarine cables stretch across oceans, linking continents and making instant global communication possible. It’s truly a marvel of engineering!
An In-Depth Guide to Networking Cables and Connectivity
Alright, let’s dive deeper into the physical world of cables and connectivity. This section is all about understanding the most common types of cables you’ll encounter, what makes them tick, and where you’ll find them. Think of it as getting to know the core components that truly make our digital world hum.
Twisted Pair Cables: The Workhorse of Modern LANs
If you’ve ever glanced behind your computer or router, chances are you’ve spotted an Ethernet cable. Well, that’s a twisted pair cable! These are, by far, the most common type of networking cable you’ll find, especially in Local Area Networks (LANs). They get their name because, inside that outer jacket, pairs of wires are literally twisted around each other.
Why the twist? It’s not just for looks! This clever engineering trick helps to cancel out electromagnetic interference (EMI) from outside sources (like power lines or microwaves) and from other wire pairs within the same cable. This “crosstalk” reduction is super important for keeping your data signals clean and clear.
You’ll typically find two main types of twisted pair cables:
- Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP): This is the most common and budget-friendly type, perfect for everyday Ethernet networks. It relies purely on the wire twisting to fight off interference.
- Shielded Twisted Pair (STP): These cables add an extra layer of protection, usually a foil or braided shield around the twisted pairs (or even each individual pair). This makes them even better at fending off EMI, which is why you might see them in electrically noisy environments or for longer cable runs.
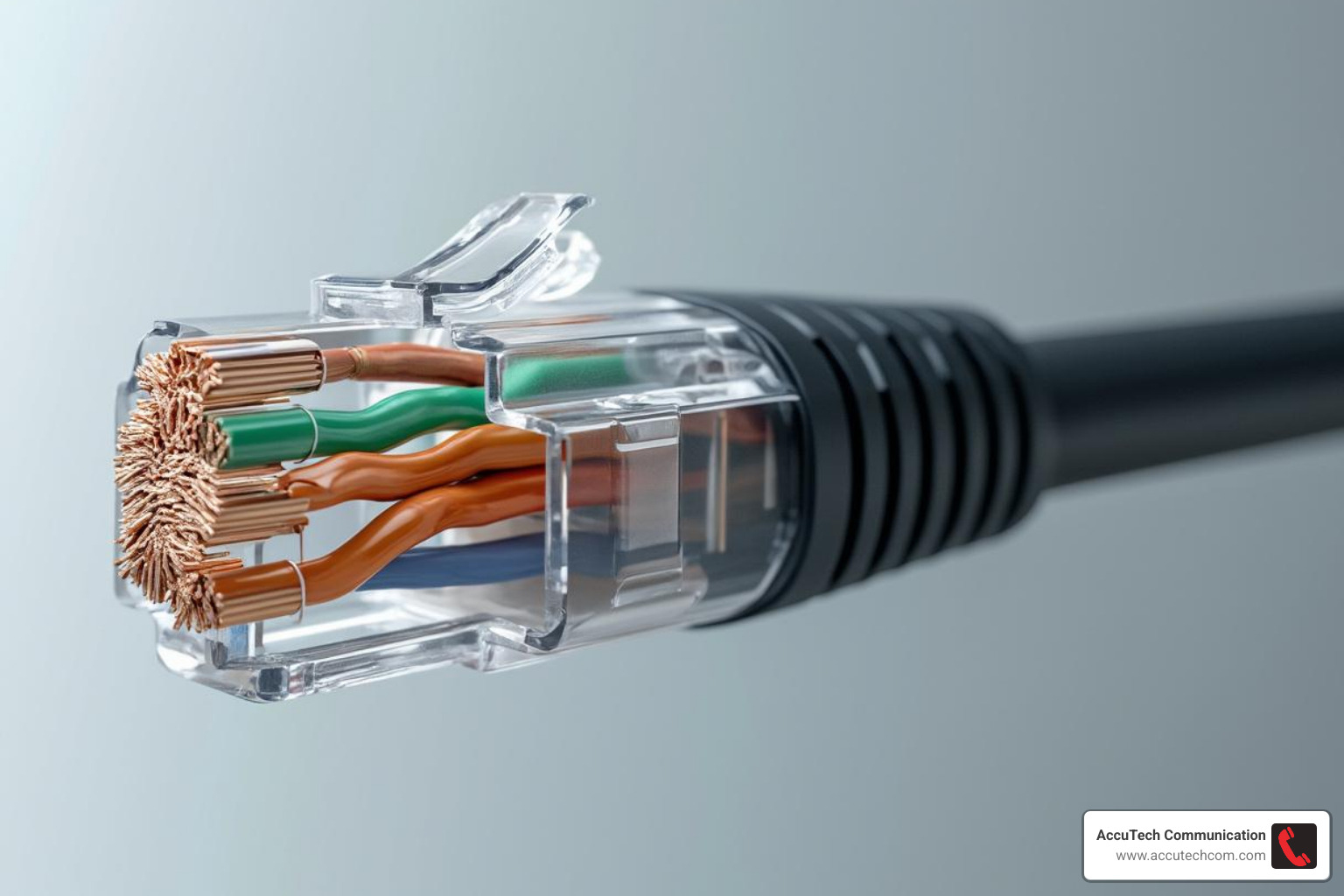
These twisted pair cables are the backbone of what we call structured cabling systems. These systems are carefully designed for reliability and easy maintenance, handling everything from the main cables connecting different floors or buildings, to the smaller “horizontal” cables that run from wiring closets right to your office wall outlets.
Here at AccuTech Communications, we specialize in network cabling installation, making sure your business gets the best performance and reliability possible.
Understanding Ethernet Cable Categories
Ethernet cables aren’t all created equal. They’re sorted into “categories” based on how fast and how much data they can handle. Think of it like different grades of highway – some are built for faster traffic and more lanes!
Let’s break down the most common ones you’ll encounter:
| Category | Speed (Gbps) | Bandwidth (MHz) | Max Length for 10G (meters) | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAT5e | 1 | 100 | 45 | Workstations, general office use, cost-effective |
| CAT6 | 1 (up to 10) | 250 | 55 | Gigabit Ethernet, future-proofing for shorter 10G runs |
| CAT6A | 10 | 500 | 100 | Data centers, aggregation links, long-distance 10G, future-proofing |
- CAT5e (Category 5e): This has been a long-standing standard for home and small business networks. It can comfortably handle speeds up to 1,000 Megabits per second (Mbps), which we often call Gigabit Ethernet. While it’s still out there, for any new installations, we usually suggest looking a bit further up the chain.
- CAT6 (Category 6): CAT6 cables are built to a higher standard, meaning they’re better at resisting interference than CAT5e. They can even reach 10 Gigabit speeds, though usually only over shorter distances (up to 55 meters). This is a solid choice for most modern gigabit networks.
- CAT6A (Category 6 Augmented): If you’re serious about 10 Gigabit Ethernet over copper, CAT6A is your champion. It supports full 10 Gbps speeds over its entire 100-meter length. It’s fantastic for data centers, connecting network switches, and anywhere you want to make sure your network is ready for the future. (Just a quick note: you might see “CAT6e” mentioned sometimes, but there’s no official standard for it – CAT6 and CAT6A are the real deals!)
- CAT7 & CAT8: These are the ultimate speed demons, often shielded, designed for even more incredible speeds and bandwidth. CAT7 can handle 10 Gbps over longer distances, and CAT8 is truly next-level, pushing 25 to 40 Gbps over shorter runs. You’ll typically find these in very specialized, high-demand settings, like connecting servers in a data center where every fraction of a second counts.
Your network will only ever be as fast as its slowest part. So, if you’ve got a super-fast CAT6 backbone but use an older CAT5e patch cable, your overall performance will be capped at CAT5e speeds. It’s like having a sports car stuck in traffic!
Coaxial Cables: From Television to Data
Coaxial cables probably look familiar if you’ve ever hooked up a TV or had cable internet. They’re most commonly used to carry television signals and connect video equipment. What makes them special is their design: they have a central conductor, surrounded by an insulating layer, which is then wrapped in a metallic shield and an outer protective jacket. This clever layering keeps the signal safely inside the cable, doing a great job of blocking outside interference.
You’ll usually see two common types:
- RG6: This is the beefier one, often used for cable television (CATV) and internet services. Its thicker conductor and better insulation allow it to carry more data over longer distances.
- RG59: Thinner and a bit more affordable than RG6, RG59 is typically used for CCTV security camera systems or shorter video connections.
Believe it or not, coaxial cables were once big players in early Ethernet networks, like the “Thicknet” and “Thinnet” systems, before twisted pair Ethernet took over. While you won’t see them in new Ethernet installations today, they’re still handy for home networking. Technologies like MoCA (Multimedia over Coax Alliance) let you use your existing coaxial TV wiring to create a high-speed home network – pretty neat, right?
Fiber Optic Cables: The Speed of Light
If you need serious speed and to cover vast distances, then fiber optic cables are your undisputed champions. Unlike traditional copper cables that rely on electrical signals, fiber optics use incredibly thin strands of glass or plastic to transmit data using pulses of light. This fundamental difference gives them some truly amazing advantages.
So, what makes fiber optics so special? Well, for starters, they offer incredible bandwidth. We’re talking about carrying vastly more data than copper – enough to make your head spin! This makes them perfect for those heavy-traffic applications and our ever-growing need for data. They also excel at long-distance transmission. Because light signals are so robust, fiber can send data over many kilometers without losing strength or needing a boost, which is brilliant for connecting distant locations or even entire cities. And here’s a big one: immunity to interference. Since they use light, fiber optic cables couldn’t care less about electromagnetic interference (EMI) or radio frequency interference (RFI) that can mess with copper lines. This means a super clean, reliable signal, even in noisy environments. Plus, there’s a strong case for data security. It’s incredibly difficult to secretly “tap” into a fiber optic cable without being detected, adding an extra layer of peace of mind for sensitive information.
You’ll find two main types of fiber optic cables:
- Single-mode Fiber (SMF): This type has a tiny core that only allows a single path for light to travel. SMF is used for extremely long distances (think many kilometers!) and super high-bandwidth applications, usually found connecting major data centers or different buildings across a large campus.
- Multi-mode Fiber (MMF): MMF has a larger core, allowing multiple paths for light. It’s generally used for shorter distances (like within a data center or inside a single building). Different versions like OM3, OM4, and OM5 offer increasing levels of performance and range.
At AccuTech Communications, we are experts in fiber optic installation, ready to provide the incredible speed and reliability your business truly needs.
Connectors, Power, and Practical Applications
Beyond the cable itself, the connectors and power delivery methods are crucial. This section covers how everything plugs together and gets powered, completing the picture of cables and connectivity.
A Guide to Common Connectors
You know how crucial the right key is for the right lock? Well, connectors are just like that for your cables! They are the vital pieces that make sure your cables properly connect to your devices. They ensure a strong, clear path for your data, and sometimes even for power.
Let’s look at a few you’re likely to see.
The RJ45 is probably the most common network connector you’ll encounter. It’s the standard plug for your Ethernet cables (like CAT5e, CAT6, and CAT6A). It has eight little wires inside and is a bit wider than a phone jack. Getting an RJ45 just right involves stripping the cable, arranging the wires in a specific order (we follow industry standards like T568A or T568B), and then using a special tool to “crimp” them into place.
Then there’s the BNC connector. You’ve likely seen these on older video equipment or CCTV cameras. They’re typically used with coaxial cables. They connect with a simple twist-and-lock motion, which is why they were popular for video signals.
And who could forget USB? This “Universal Serial Bus” is everywhere! From charging your phone to connecting your keyboard, mouse, or printer, USB connectors are incredibly versatile. You’ll find them in many shapes and sizes, like the classic USB-A, the smaller Micro-USB on older phones, and the modern, reversible USB-C that can handle fast data and power.
Finally, when we talk about fiber optics, we enter a world of very precise connectors. These need to perfectly align tiny glass strands to send light signals. Some common types include the SC (Subscriber Connector), which snaps into place; the older ST (Straight Tip), which twists on; and the tiny LC (Lucent Connector), which is great for tight spaces in data centers. For super high-density networks, you might even see MPO (Multi-fiber Push-on) connectors, which bundle many fibers into one compact plug.
Choosing the right connector and making sure it’s installed perfectly is a big part of having a reliable network. It’s all about making those digital connections solid!
Power over Ethernet (PoE) vs. Power over Cable (PoC)
Imagine you could power a security camera or a desk phone with the same cable that gives it internet! That’s not magic; that’s the clever technology behind sending both power and data over a single wire.
This is exactly what Power over Ethernet (PoE) does. It’s a widely used standard that lets devices get electrical power and data through just one Ethernet cable. This means fewer cables, fewer power outlets needed, and simpler installations for things like VoIP phones, IP cameras, and wireless access points. PoE follows strict industry standards for voltage (usually between 37 and 57 volts), which makes it safe and compatible across many different brands. It’s a huge help for businesses looking to keep their cabling neat and efficient.
Now, you might also hear about Power over Cable (PoC). While it sounds similar, PoC is quite different. It’s not a widely accepted standard like PoE. Instead, PoC usually refers to proprietary systems, meaning they’re custom-made for specific products or manufacturers. You might see PoC in specialized audio-visual setups, but it’s often limited in how it works with other devices.
For most modern business needs, especially when combining power and data over your network, PoE is the reliable, standardized choice. It’s built for compatibility and safety.
The Structure of a Professional Network: Patch Cables and Structured Cabling
Building a reliable network is like building a house. You don’t just throw up some walls; you need a strong, organized foundation. In cables and connectivity, this means understanding the difference between patch cables and structured cabling.
Think of patch cables as the short, flexible cords that make quick connections. They’re often colorful and used to link a computer to a wall outlet, or a server to a switch. They’re designed to be easily moved and changed as your needs shift. While a CAT5e patch cable typically works at 350 MHz, a CAT6 version operates at 550 MHz, giving you more bandwidth for those quick links.
But below those patch cables lies something much more permanent: structured cabling. This is the hidden highway system of your building. It’s a comprehensive, organized wiring infrastructure that’s designed to support everything from your computers and phones to security cameras and Wi-Fi access points.
The core idea of structured cabling is to install a network that lasts for many years, even as your technology changes. It includes components like patch panels (centralized connection points), wall outlets in offices, and both backbone cabling (connecting different floors or buildings) and horizontal cabling (running from wiring closets to individual rooms).
The main difference? Patch cables are for temporary connections, while structured cabling is the permanent, underlying network of your building. Structured cabling is a smart, long-term investment because it offers amazing scalability (easy to add new devices) and simplifies maintenance. If you need to move a desk or upgrade equipment, a well-planned structured cabling system makes it a breeze.
At AccuTech Communications, we specialize in designing and installing these robust foundations. We provide comprehensive structured cabling services to ensure your business has a reliable and future-proof network.
Frequently Asked Questions about Cables and Connectivity
Navigating cables and connectivity can sometimes feel like learning a new language! But don’t worry, we’re here to break down some of the most common questions we hear, making it simple and clear.
Which Ethernet Cable is Best for My Business?
Ah, the million-dollar question! The “best” Ethernet cable truly depends on your business’s unique needs today and where you plan to be tomorrow. It’s like choosing the right vehicle – a sports car isn’t always best for hauling cargo, right?
For most everyday office workstations, where you’re just browsing, emailing, and using standard applications, a CAT5e cable will likely give you all the performance you need. It comfortably supports Gigabit Ethernet (1,000 Mbps), which is plenty fast for typical tasks.
However, if you’re setting up a new office, or simply want a bit more future-proofing and better performance, CAT6 is a fantastic standard. It handles today’s gigabit speeds with ease and offers improved protection against crosstalk and signal noise. Think of it as a reliable, high-performance sedan for your data.
Now, if you’re a business with high-bandwidth demands – perhaps you’re handling large video files, running a data center, or just want to be absolutely ready for whatever the future throws at you – then CAT6A is your champion. This cable reliably supports blazing-fast 10-Gigabit Ethernet over its full length. It’s the ideal choice for new constructions and critical backbone links between your network switches. Investing in CAT6A now can save you significant time and money down the road, as you won’t need to re-cable when speeds inevitably increase.
What is the Main Advantage of Fiber Optic Cable?
If copper cables are the workhorses, then fiber optic cables are the speed demons of the cables and connectivity world! Their main advantages boil down to three superpowers: speed, bandwidth, and distance.
Unlike traditional copper cables that send data using electrical signals, fiber optic cables transmit information using incredibly fast pulses of light through thin strands of glass or plastic. This fundamental difference means they can carry a monumental amount of data – we’re talking terabits per second! – and send it over much longer distances, often many kilometers, without losing signal strength.
Another huge benefit? Fiber optic cables are completely immune to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI). So, in electrically “noisy” environments, or when you need absolute reliability, they shine. This makes them the ultimate choice for critical connections like data center backbones, linking buildings across a campus, or anywhere maximum speed and unwavering reliability are non-negotiable.
Can I Use My Home’s Existing Wiring for a Network?
It’s a clever thought, and the answer is yes, sometimes! There are indeed technologies that allow you to piggyback a network onto wiring already present in your home.
For example, Powerline Communication (PLC) lets you use your home’s electrical wiring to send network data. The ITU-T G.hn standard, for instance, developed in 2008, was designed for high-speed communication over existing power lines, and it even includes ways to use old phone and coaxial cables. Then there’s Ethernet over Coax (MoCA), which turns your TV’s coaxial cables into a network backbone. And yes, some technologies can even leverage older phone lines for data.
These solutions can be super convenient for homeowners, especially when pulling new Ethernet cables through walls isn’t practical. However, for a business setting, these options typically offer lower performance and reliability compared to dedicated networking infrastructure. They can be prone to interference, speed fluctuations, and are harder to troubleshoot.
For business-grade reliability, consistent speed, and long-term scalability, dedicated structured cabling (using those trusty twisted pair or super-fast fiber optic cables) is always the superior choice. It provides a stable, predictable foundation that your business can truly rely on, today and tomorrow.
Conclusion: Building a Reliable and Future-Proof Network
Think of your business as a well-oiled machine. Every part, every process, needs to work together seamlessly. At the heart of that seamless operation, especially in our digital age, lies your network. It’s the invisible, yet incredibly vital, highway system that carries all your critical information. And guess what? That highway system relies heavily on the quality of its cables and connectivity.
Choosing the right cabling and connectivity solutions isn’t just about plugging things in; it’s a strategic investment in your organization’s future. It’s about ensuring your team can work without frustrating delays, that your business phone calls are crystal clear, and that your data flows effortlessly. Whether it’s ensuring minimal latency for your business phone system or building a robust data center that can handle tomorrow’s demands, a reliable physical network infrastructure is the unseen hero that keeps your productivity humming.
We know that navigating network cabling can feel a bit daunting. There are so many options, so many technical terms! That’s where a trusted partner comes in. For businesses across Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Rhode Island, AccuTech Communications has been that reliable expert since 1993. We don’t just install cables; we design and implement certified, high-quality solutions custom to your unique needs, ensuring your network is built to last and to perform.
We’re here to help you build the robust foundation your business needs to thrive, now and in the future. Let us take the complexity out of your network infrastructure so you can focus on what you do best. Ready to chat about your commercial network cabling needs? We’d love to hear from you. Contact us to discuss your commercial network cabling needs.