Fiber Optic Sensing Technology: Top 3 Powerful Benefits
Fiber optic sensing technology is a game-changing innovation that allows us to “see” the unseen by transmitting information as light pulses through hair-thin fibers of glass or plastic. This technique leverages the extraordinary properties of light to detect changes in temperature, strain, and vibration, enabling businesses to monitor their infrastructure more accurately and in real-time. Whether used in healthcare facilities or large telecommunication networks, fiber optic cables provide superior bandwidth and reliability compared to traditional copper wires. They transform the way businesses maintain communication systems, ensuring seamless and efficient operations.
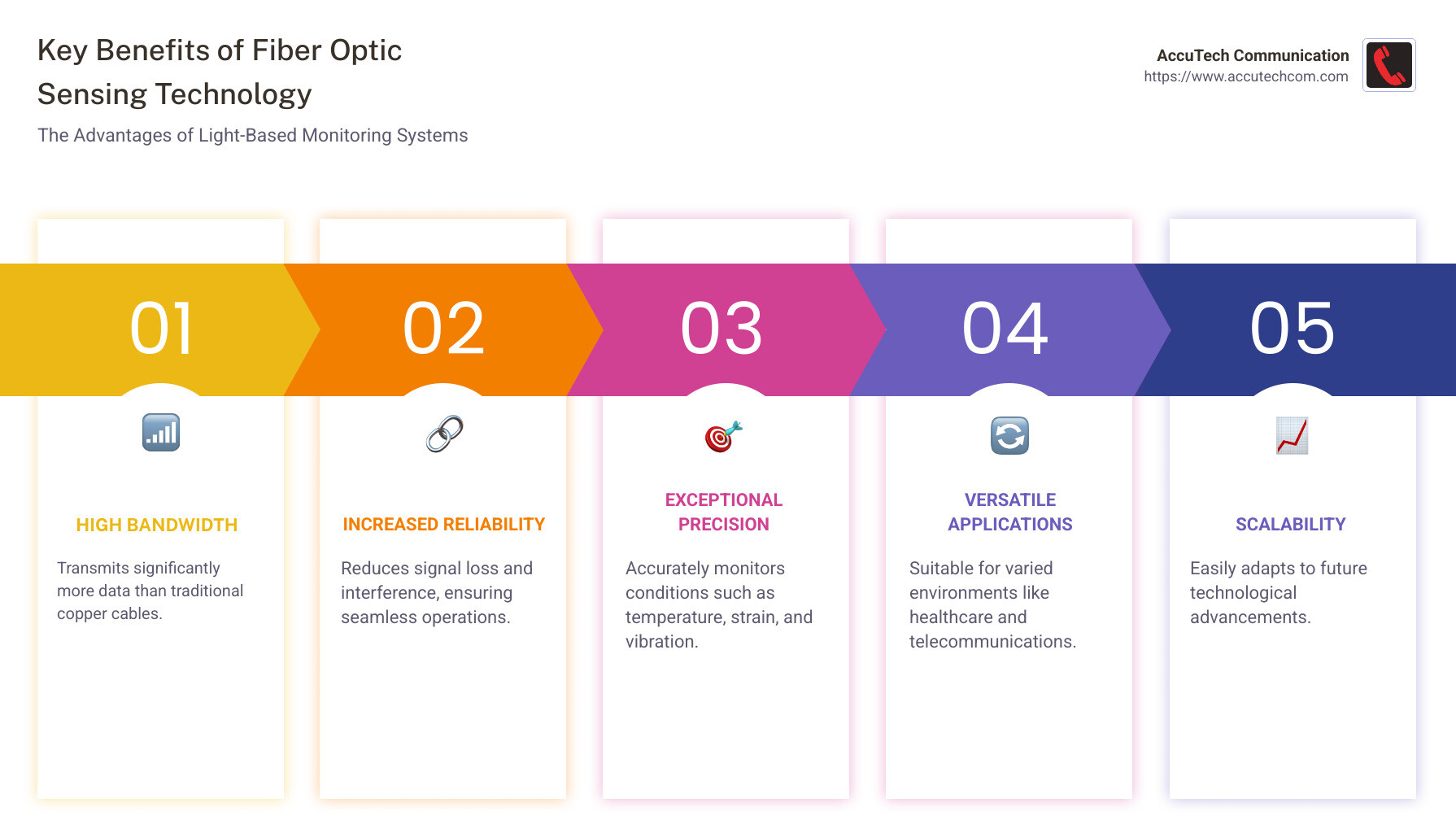
As you explore fiber optic sensing technology, you will find its profound impact on sectors from healthcare to telecommunications, offering robust solutions for network challenges and helping businesses stay ahead. Here are the key aspects:
- Higher Bandwidth: Transmits more data than traditional copper cables.
- Reliability: Reduced signal loss and interference, ensuring continued operations.
- Precision: Monitors conditions with high accuracy.
- Versatility: Suitable for varied environments and applications.
- Scalability: Adapts to future technological advancements.
I’m Corin Dolan, and with a rich background in fiber optic sensing technology, I’ve helped businesses across Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Rhode Island tailor their communication systems for optimal performance. Let’s dig further to understand how this technology can illuminate the invisible aspects of your operations and ensure your network infrastructure remains reliable and efficient.
Fiber optic sensing technology definitions:
– fiber optic cable technology
– fiber optic monitoring system
Understanding Fiber Optic Sensing Technology
Fiber optic sensing technology uses the physical properties of light to detect changes in the environment. This involves measuring variations in temperature, strain, and vibrations along an optical fiber. Here’s how each aspect works:
Temperature Detection
Fiber optic sensors can detect temperature changes with incredible precision. This is achieved through techniques like Raman scattering, where the interaction of light with the fiber material changes with temperature. By measuring these changes, sensors can accurately determine temperature variations along the fiber. This is crucial for applications like monitoring power cables for hotspots, ensuring safety and efficiency.
Strain Measurement
Strain measurement is vital for infrastructure monitoring. Brillouin scattering is a key method used in fiber optic sensing for this purpose. When light travels through an optical fiber, any strain or pressure alters the light’s properties. By analyzing these changes, fiber optic sensors can detect even minute deformations. This helps in predicting structural weaknesses before they become critical issues.
Vibration Sensing
Vibration sensing is another critical application of fiber optic technology. Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) is used to detect vibrations along a fiber. This technology can identify and locate disturbances, such as unauthorized digging near pipelines or changes in ground movement. It acts like a long, continuous microphone, providing real-time data over vast distances.
Fiber optic sensing technology is changing industries by providing real-time, accurate monitoring. It allows businesses to quickly respond to changes, reducing risks and enhancing operational efficiency. Whether it’s detecting temperature fluctuations, measuring strain in bridges, or sensing vibrations in seismic areas, this technology offers a window into the invisible world around us.
Types of Fiber Optic Sensing
Fiber optic sensing technology is versatile, offering various methods to monitor different environmental factors. Let’s explore three key types: Distributed Temperature Sensing (DTS), Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS), and Distributed Strain Sensing (DSS).
Distributed Temperature Sensing (DTS)
DTS uses the principles of Raman scattering to monitor temperature changes along an optical fiber. When light travels through the fiber, interactions with the material cause shifts in the light’s properties, which vary with temperature. These changes are detected and analyzed, allowing DTS systems to identify hotspots and temperature variations with precision. This capability is invaluable in applications like power cable monitoring, where detecting overheating can prevent failures and improve safety.
Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS)
DAS transforms a fiber optic cable into a sensitive vibration detector. Using coherent Rayleigh backscattering, DAS systems can “hear” vibrations along the fiber’s length. This technology acts like a continuous microphone, capable of detecting and locating disturbances such as unauthorized digging near pipelines or seismic activity. Real-time data from DAS systems enables rapid response to potential threats, enhancing security and safety in critical infrastructure.
Distributed Strain Sensing (DSS)
DSS employs Brillouin scattering to measure strain along optical fibers. When a fiber experiences strain, the properties of the light traveling through it change. By analyzing these changes, DSS systems can detect even slight deformations in structures like bridges or buildings. This early detection helps prevent structural failures by allowing maintenance before problems escalate. DSS is a powerful tool for infrastructure monitoring, ensuring long-term safety and reliability.
Each type of fiber optic sensing offers unique benefits, making them essential tools for modern monitoring and safety solutions. These technologies provide a comprehensive view of the environment, helping industries respond proactively to changes and maintain operational efficiency.
Applications of Fiber Optic Sensing Technology
Fiber optic sensing technology is like having a superpower for monitoring and protecting our world. Let’s explore some of its coolest applications: infrastructure monitoring, leak detection, seismic activity, and smart cities.
Infrastructure Monitoring
Imagine a bridge that can tell you when it’s starting to feel stressed. With fiber optic sensing, that’s possible. By embedding fibers into structures like bridges, dams, and pipelines, we can continuously monitor their health. When there’s a change in temperature, strain, or vibration, the system sends out alerts. This real-time monitoring helps prevent disasters by catching problems early.
Example: In pipelines, fiber optic sensors can detect ground movement or third-party interference, ensuring the pipeline remains safe and secure.
Leak Detection
Leaks can be sneaky and damaging, whether they’re in oil pipelines or water systems. Fiber optic sensing technology helps detect leaks quickly by sensing changes in temperature or pressure. This early detection means faster repairs and less environmental damage.
Case Study: Using Distributed Temperature Sensing (DTS), companies can pinpoint the exact location of a leak along a pipeline. This precision saves time and resources, reducing the mean time to repair (MTTR).
Seismic Activity
Earthquakes are unpredictable, but with fiber optic sensors, we can get a head start. Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) turns fiber optic cables into a network of tiny seismometers. These sensors detect vibrations and seismic waves, providing valuable data for early warnings.
Real-World Impact: Undersea cables have been repurposed to detect underwater earthquakes, potentially providing crucial warning time for tsunamis. This technology could save lives by alerting people sooner.
Smart Cities
Smart cities use technology to improve urban life, and fiber optic sensing is a key player. By integrating sensors into city infrastructure, we can monitor traffic flow, detect structural issues, and even manage utilities more efficiently. This data-driven approach helps cities become more sustainable and responsive.
Vision: Imagine a city where streetlights adjust based on traffic flow or water usage is optimized in real-time. Fiber optic sensing makes these innovations possible, paving the way for smarter, more connected communities.
Fiber optic sensing technology is changing the way we monitor and protect our world. From bridges to pipelines, and even entire cities, these sensors provide the data we need to make informed decisions and keep people safe.
How Fiber Optic Sensing Works
Fiber optic sensing is a fascinating process that relies on the interaction of light with the fiber itself. This interaction is primarily based on three types of scattering: Rayleigh scattering, Raman scattering, and Brillouin scattering. Each plays a unique role in how we detect and measure different environmental changes.
Rayleigh Scattering
Rayleigh scattering is the backbone of Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS). When light travels through an optical fiber, it encounters tiny imperfections in the fiber. These imperfections scatter the light in different directions. By analyzing these scattered light patterns, we can detect vibrations and acoustic waves along the fiber’s length. This makes Rayleigh scattering perfect for monitoring vibrations caused by seismic activity or traffic movement.
Raman Scattering
Raman scattering is key to Distributed Temperature Sensing (DTS). It occurs when light interacts with the molecular vibrations of the fiber material. This interaction causes a shift in the light’s wavelength, which is sensitive to temperature changes. By measuring these shifts, we can accurately determine the temperature along the fiber. This capability is crucial for applications like leak detection in pipelines or temperature monitoring in data centers.
Brillouin Scattering
Brillouin scattering is used in Distributed Strain Sensing (DSS). It involves the interaction of light with sound waves within the fiber. When the fiber experiences strain or stress, the frequency of the scattered light changes. By measuring these frequency shifts, we can assess strain and structural integrity over long distances. This is particularly useful for infrastructure monitoring, such as detecting deformations in bridges or buildings.

In summary, fiber optic sensing technology leverages these scattering effects to provide continuous and accurate monitoring of environmental conditions. By understanding how light interacts with the fiber, we can extract valuable data that helps protect and optimize our infrastructure.
Next, let’s explore the advantages and disadvantages of using fiber optic sensors in various applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Fiber Optic Sensors
Fiber optic sensing technology offers several compelling benefits, making it a popular choice for a variety of applications. However, like any technology, it also has its drawbacks. Let’s explore the pros and cons.
Advantages
1. Real-Time Monitoring
Fiber optic sensors excel at providing continuous, real-time data. This capability is crucial for applications that demand immediate feedback, such as infrastructure monitoring and power utilities. By integrating these sensors, organizations can detect issues like overheating or mechanical strain before they escalate into major problems, allowing for proactive maintenance and reducing downtime.
2. High Precision
Another standout feature of fiber optic sensors is their high precision. These sensors can detect minute changes in temperature, strain, and vibration with remarkable accuracy. For instance, in seismic activity monitoring or leak detection, even the slightest variations can be critical. The ability to pinpoint these changes helps in making informed decisions quickly.
Disadvantages
1. Temperature Limitations
Despite their many benefits, fiber optic sensors do have some limitations. One of the main challenges is their sensitivity to temperature. While fiber optic sensors can measure temperature changes, extreme temperatures can affect their performance. This can be a concern in environments where temperatures fluctuate significantly or reach extremes.
2. Fragility and Installation Complexity
Fiber optic cables, while robust in many aspects, are also quite fragile. They require careful handling and protection, especially during installation. The process can be labor-intensive and requires specialized knowledge and tools, which can increase costs and time for deployment.
In conclusion, while fiber optic sensing technology offers numerous advantages such as real-time monitoring and high precision, it also presents challenges like temperature sensitivity and installation complexity. Understanding these factors is essential for making informed decisions about their use in various applications.
Next, we’ll address some frequently asked questions about fiber optic sensing technology to further clarify its capabilities and limitations.
Frequently Asked Questions about Fiber Optic Sensing Technology
What is fiber optic sensing technology?
Fiber optic sensing technology uses light waves to detect changes in the environment, such as temperature, strain, and vibration. Imagine a slender, transparent thread that can “see” what’s happening around it. This is thanks to the physical properties of light, which travels down the optical fiber and reacts to changes along its path. The result is high precision data that can be used for real-time monitoring in various applications, from infrastructure to seismic activity.
What are the disadvantages of fiber optic sensors?
While fiber optic sensors are incredibly precise, they aren’t without their challenges:
- Temperature Limitations: These sensors can be sensitive to extreme temperatures, which might affect their accuracy. In environments where temperatures swing wildly, this can be a concern.
- Operating Band: Fiber optic sensors operate within specific light wave bands. If the conditions push these boundaries, the sensors might not perform optimally.
- Fragility: The fibers themselves are delicate and require careful handling during installation. Bending or breaking can lead to signal loss.
- Installation Complexity: Setting up fiber optic systems can be labor-intensive and requires skilled technicians, which can drive up costs and time.
Is fiber optic certification worth it?
Becoming a Certified Fiber Optic Technician is highly valuable in the industry. It signifies a deep understanding of fiber optic systems and ensures that installations meet high standards. Industry recognition of this certification can open doors to numerous job opportunities, especially in regions like Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and New Hampshire, where fiber optics are in demand. Certification not only boosts your credentials but also assures clients of your expertise and commitment to quality.
Understanding these aspects of fiber optic sensing technology helps in making informed decisions about its deployment and use. In the next section, we’ll explore the various applications where this technology shines.
Conclusion
At AccuTech Communications, we pride ourselves on our commitment to quality and providing competitive pricing for our clients in Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Rhode Island. Since 1993, we’ve been dedicated to offering reliable and certified services that meet the highest industry standards.
Our focus on quality means that we ensure every fiber optic installation is performed by skilled technicians who understand the intricacies of this technology. This commitment guarantees that our clients receive the best possible service and results. Whether it’s network cabling, business phone systems, or data center technologies, we deliver solutions that are both effective and efficient.
Competitive pricing is another cornerstone of our service. We believe that high-quality fiber optic solutions should be accessible to all businesses, regardless of size. By maintaining competitive pricing, we enable more businesses to benefit from the advanced capabilities of fiber optic sensing technology.
When connectivity and real-time monitoring are increasingly crucial, AccuTech Communications stands out as a leader in providing cutting-edge solutions. Our expertise in fiber optic sensing technology ensures that our clients can leverage this powerful tool for applications ranging from infrastructure monitoring to smart city development.
For more information about our services and how we can help your business harness the power of fiber optics, visit our Fiber Optic Cable Services page. Join us at AccuTech Communications, where quality meets affordability, and innovation drives success.

