Office Cabling: 10 Powerful Tips for a Successful 2025 Setup
Why Office Cabling Is the Backbone of Modern Business Success
Office Cabling is the structured network of cables, connectors, and hardware that connects all your computers, phones, security systems, and smart devices throughout your building. Think of it as the nervous system of your business—when it works well, everything flows smoothly. When it doesn’t, productivity grinds to a halt.
Quick Office Cabling Overview:
– What it includes: Data cables (Cat5e, Cat6, fiber), voice lines, security wiring, and wireless access points
– Why it matters: Supports internet, phone systems, WiFi, security cameras, and IoT devices
– Typical lifespan: 10-15 years with proper installation
– Key benefit: Reduces downtime and supports business growth
– Professional vs. DIY: Certified installers provide warranties and ensure compliance
As one installer recalled from the research: “Unlabeled cables are one of the worst installation oversights an IT team can face.” Poor cabling doesn’t just look messy—it causes downtime, safety risks, and expensive troubleshooting headaches.
Modern businesses demand more from their buildings. Spaces need to adapt quickly to changing requirements, support remote work technology, and integrate smart building systems—all while maintaining rock-solid reliability for critical operations like healthcare monitoring or financial transactions.
I’m Corin Dolan, owner of AccuTech Communications, and I’ve been designing and installing Office Cabling systems across Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Rhode Island since 1993. My team has helped hundreds of businesses—from hospitals to manufacturing facilities—build reliable, future-proof networks that grow with their needs.

Office Cabling terms to learn:
– backbone cabling
– fiber optic cable
– types of cables
Office Cabling 101: What It Is and Why It Matters
Think of Office Cabling as the circulatory system of your business. Just like your body needs blood vessels to carry oxygen to every organ, your office needs cables to carry data to every device. When that system works smoothly, everything hums along perfectly. When it doesn’t, well… let’s just say nobody gets much work done.
Office Cabling is the organized network of cables, connectors, and hardware that connects all your business technology—computers, phones, security cameras, WiFi access points, and those smart thermostats that somehow know exactly when you walk into a room. Modern businesses depend on structured cabling systems because they’re the foundation that makes everything else possible.
Here’s what a properly designed system delivers: uptime reliability that reduces network failures by up to 60%, productivity gains because your team isn’t constantly dealing with “my internet is down” complaints, and cost savings from dramatically reduced troubleshooting time. You also get scalability that makes adding new devices as simple as plugging them in, rather than calling in a crew to run new cables through your walls.
The system supports unified communications like VoIP phone systems and video conferencing, while also being IoT ready for smart building technologies. Most importantly, professional installations ensure compliance with safety codes and industry standards—something that matters more than you might think when insurance companies come calling.
A well-designed Office Cabling system typically supports growth for 5 to 10 years. That forward-thinking approach protects your investment and saves you from the headache of frequent upgrades every time technology takes another leap forward.
“Office Cabling” vs. Traditional Point-to-Point
Picture the worst cable management you’ve ever seen—cables snaking under desks, tangled behind equipment, held together with twist ties and hope. That’s traditional point-to-point cabling, where each device connects directly to another device or central hub. We call this “patch chaos,” and trust me, it’s as bad as it sounds.
Office Cabling takes a completely different approach. Instead of cables running everywhere like digital spaghetti, structured systems follow organized pathways to centralized connection points. Think of it like the difference between a city with planned streets versus one where people just wandered around and eventually wore paths in the dirt.
When you need to move a workstation or add a new device, you’re making simple changes at a patch panel rather than pulling new cables through walls and ceilings. This organized approach can reduce the time and costs of network changes by up to 60%—which means less disruption to your business and fewer surprise bills from your IT team.
Six Building Blocks of a Structured Cabling System
Every professional Office Cabling installation follows the same six-component blueprint. These aren’t arbitrary choices—they’re industry standards that ensure your system works reliably and can be maintained by any qualified technician.
The entrance facility is where the outside world connects to your building—fiber internet, phone lines, and cable services all come through here. It’s like the front door for all your telecommunications services.
Your equipment room serves as mission control, housing the main network equipment like switches, routers, and servers. This needs to be a dedicated, climate-controlled space with proper power and ventilation, because nobody wants their server rack turning into an expensive space heater.
Backbone cabling creates the main data highways connecting your equipment room to telecommunications rooms throughout your building. These are typically fiber optic cables that can handle high-speed, long-distance connections without breaking a sweat.
Each floor or major section gets its own telecommunications room—smaller network closets that house the equipment connecting backbone cabling to individual work areas. Think of these as neighborhood distribution centers in your building’s data delivery system.
The horizontal cabling system runs from those telecommunications rooms to individual work areas. Most offices use twisted pair cables like Cat5e, Cat6, or Cat6a for reliable data transmission up to 100 meters—which covers pretty much any office layout you can imagine.
Finally, the work area is where your employees actually plug in their devices. This includes wall plates, patch cords, and that crucial first six feet of cable from the wall to someone’s laptop. It might seem simple, but proper work area design makes the difference between a system that works seamlessly and one that drives everyone crazy.
Choosing the Right Cable Types for Your Workplace
When I walk into a new client’s office for a consultation, one of the first questions they ask is: “What kind of cables do we actually need?” It’s a great question because choosing the right cables for your Office Cabling system can make the difference between a network that serves you well for a decade and one that needs expensive upgrades in just a few years.
The truth is, there’s no one-size-fits-all answer. Your cable selection depends on your current bandwidth needs, growth plans, budget constraints, and the specific applications you’ll be running. A law office with basic internet and email needs has very different requirements than a design firm transferring massive video files or a manufacturing facility with IoT sensors throughout the building.
Let me break down your options in plain English, so you can make informed decisions that protect your investment.
Copper Ethernet: Cat5e to Cat7 Explained
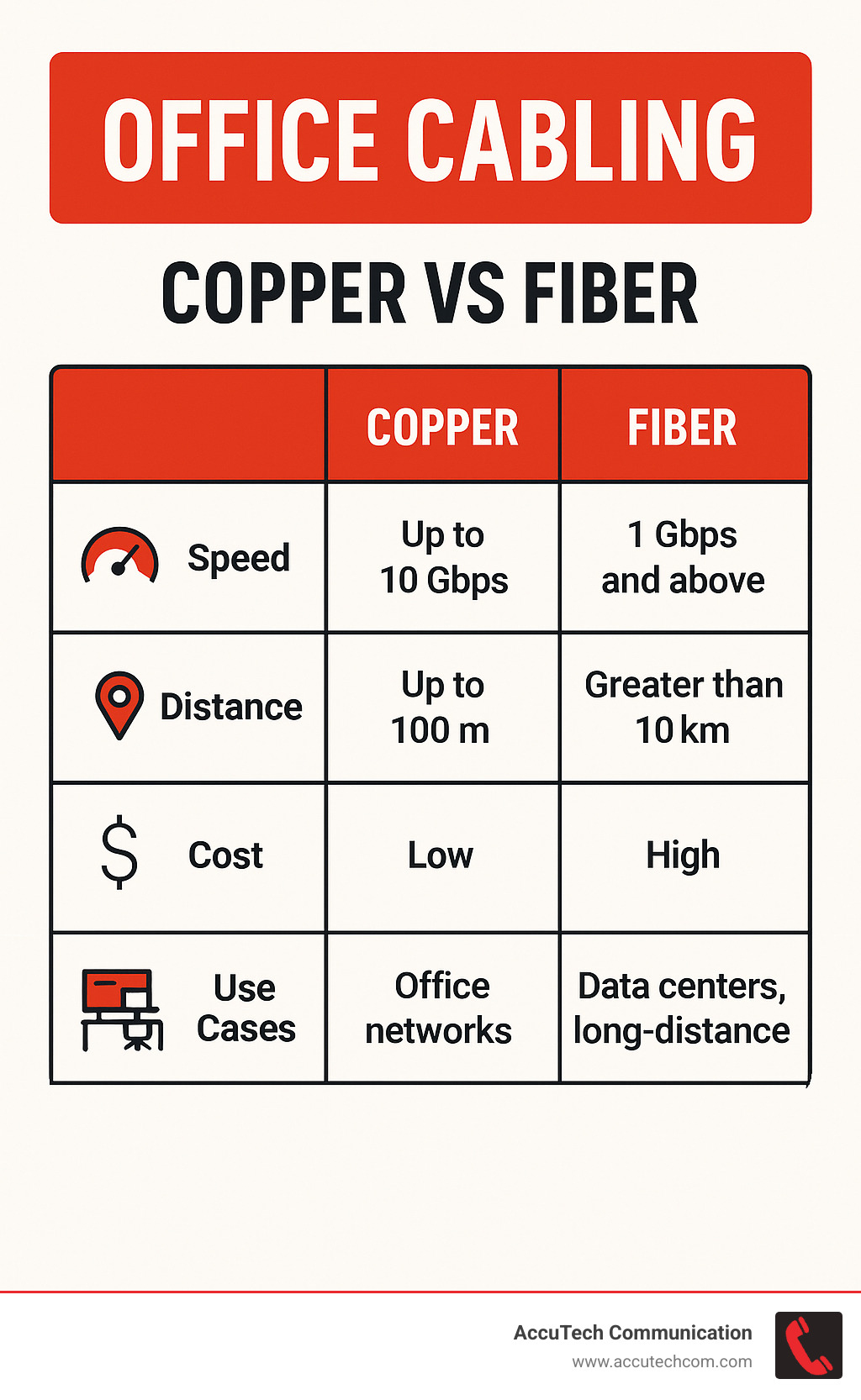
Copper cables are still the backbone of most office installations, and for good reason. They’re reliable, cost-effective, and handle the majority of business applications beautifully. Think of them as the reliable workhorse of your Office Cabling system.
Cat5e remains the most economical choice for basic business needs. It supports speeds up to 1 Gbps over 100 meters, which is more than adequate for standard internet browsing, email, and file sharing. It also supports basic Power over Ethernet (PoE) at 15.4 watts, which can power simple devices like basic IP phones and some wireless access points.
Cat6 cables step things up significantly. They can handle up to 10 Gbps speeds, though only at shorter distances of 55 meters. For the full 100-meter run, you’ll get reliable 1 Gbps performance. The real advantage comes with PoE+ support at 25.5 watts, which opens up options for more sophisticated devices like advanced security cameras and high-powered wireless access points.
Cat6a (the “a” stands for “augmented”) is where future-proofing really kicks in. These cables maintain 10 Gbps speeds for the full 100-meter distance and include better shielding against electromagnetic interference. They support PoE++ up to 60 watts, which means you can power demanding devices like PTZ security cameras and high-performance wireless equipment. While they cost more upfront, they often provide the best long-term value.
Cat7 represents the premium option with speeds up to 40 Gbps and excellent EMI protection. However, most businesses find Cat6a provides the sweet spot between performance and cost for typical office applications.
All copper cables share the same 100-meter distance limitation. Beyond 328 feet, you’ll need repeaters or should consider fiber optic alternatives.
Fiber Optic Backbones for High-Speed & Long Runs
Fiber optic cables are like the superhighway of Office Cabling—they handle massive amounts of data over incredible distances without breaking a sweat. Instead of electrical signals traveling through copper, fiber uses light pulses traveling through incredibly thin glass or plastic strands.
The performance numbers are impressive: speeds up to 100 Gbps and distances up to 80 kilometers. But the real-world benefits go beyond raw speed. Fiber is completely immune to electromagnetic interference, which means your network won’t be affected by electrical equipment, radio signals, or even lightning strikes.
Security is another major advantage. It’s extremely difficult to tap into fiber optic cables without detection, making them ideal for sensitive business communications. Plus, they’re future-proof in a way that copper simply can’t match—the bandwidth capacity far exceeds anything we’re likely to need in the foreseeable future.
You’ll encounter two main types: single-mode fiber for longer distances up to 80 kilometers and higher speeds, and multi-mode fiber for shorter distances up to 2 kilometers but at lower cost and easier installation. For most office buildings, multi-mode fiber provides excellent performance for backbone connections between network closets.
Fiber optic cables excel at connecting separate buildings, linking telecommunications rooms throughout large facilities, and supporting bandwidth-intensive applications like high-definition video conferencing and large file transfers.
Speciality & Legacy Cables You’ll Still See Around
Even in the most modern Office Cabling installations, you’ll encounter several specialty cable types that serve specific purposes or support legacy systems.
Coaxial cables remain common for certain applications, particularly security camera systems and cable TV connections. You’ll typically see RG59 and RG6 varieties, with RG6 being the more modern standard. These cables can reliably carry signals up to 500 meters and are still the preferred choice for many surveillance systems.
Telephone cables include older Cat3 cables and newer Cat5 installations for traditional landline systems. While many businesses have moved to VoIP systems that use standard ethernet cables, maintaining some traditional phone infrastructure often makes sense for backup communications during internet outages.
Patch cords are the short cables—typically one to ten feet long—that connect your devices to wall outlets. They’re available in all cable categories and are essential for network flexibility. Having quality patch cords makes moves, adds, and changes much easier and helps maintain the performance characteristics of your cabling system.
Adapters and converters bridge different cable types and standards. These include fiber-to-copper converters, USB adapters, and various connectors that help during system transitions and upgrades. While not glamorous, they’re often essential for maintaining compatibility between old and new equipment.
The key is understanding which cables serve your specific needs while planning for future growth. A well-designed system combines different cable types strategically, using each where it performs best and provides the most value.
Designing a Future-Proof Structured Cabling System
Building an Office Cabling system that serves your business well for the next decade requires thinking beyond today’s needs. I’ve seen too many companies install systems that work perfectly on day one but become bottlenecks within just a few years. The secret is designing with scalability, modularity, and smart integration from the start.

The foundation of future-proof design starts with scalability. I always recommend planning for 150-200% of your current needs. If you have 50 employees today, design your system for 100-150 connections. This might seem excessive, but it’s far less expensive to install extra capacity upfront than to tear open walls later when your business grows.
Modularity makes all the difference when changes are needed. Using standardized components like patch panels, modular jacks, and structured cable pathways means you can reconfigure connections quickly without major rewiring projects. I’ve watched companies save thousands of dollars simply because their original installer chose modular components over fixed connections.
Integration planning prevents headaches down the road. Your Office Cabling system needs to support data, voice, security cameras, fire safety systems, and building automation—all at the same time. When these systems share pathways and infrastructure, installation costs drop significantly and future maintenance becomes much simpler.
Standards compliance isn’t optional—it’s essential. Following TIA/EIA and ANSI standards ensures your cables will work with equipment from any manufacturer and meet performance specifications. These standards also cover critical safety requirements like fire ratings for different building spaces.
Speaking of fire safety, plenum-rated cables are required in air-handling spaces while riser-rated cables must be used in vertical runs between floors. Using the wrong cable type isn’t just poor practice—it violates building codes and creates serious safety risks.
Space planning and heat load management become critical in larger installations. Cable bundles generate heat, and proper cable tray systems with adequate spacing prevent overheating that can degrade performance or create fire hazards. More info about Structured Cabling Installation covers these technical requirements in detail.
How Zone Cabling Enables Smart Buildings & Agile Workspaces
Zone cabling represents a smart evolution in office design that’s perfect for today’s flexible workspaces and smart building technologies. Instead of running every cable directly from the main telecommunications room to each workstation, zone cabling creates intermediate consolidation points throughout your space.
Think of it like having neighborhood distribution centers instead of shipping everything from one central warehouse. These consolidation points—typically located in ceiling spaces or under-floor areas—serve smaller zones within your office. This approach dramatically reduces the complexity and cost of moves, adds, and changes.
The benefits become obvious quickly. Faster deployment happens because shorter cable runs are quicker and less expensive to install. Easier changes mean moving or adding workstations only affects the local zone, not the entire building infrastructure. Most importantly, zone cabling naturally supports IoT devices like sensors, lighting controls, and HVAC systems that make buildings smarter and more efficient.
Cost reduction adds up over time. When you need to reconfigure space, changes stay isolated to specific zones rather than requiring work throughout the entire building. I’ve seen companies reduce their network change costs by 60% simply by implementing zone cabling during their initial installation.
Latest research on zone cabling confirms it’s becoming the preferred approach for open offices and smart buildings where devices need frequent reconfiguration. The flexibility matches how modern businesses actually work—with teams that change, spaces that adapt, and technology that evolves.
Smart building integration becomes seamless with zone cabling. Each zone can include both active consolidation points (with power for switches and wireless access points) and passive consolidation points (simple connection hubs). This flexibility supports current smart building technologies while leaving room for innovations we haven’t imagined yet.
Planning for WiFi, VoIP, Security & IoT on Day One
Modern Office Cabling systems must juggle multiple technologies simultaneously, and planning for this integration from the beginning saves both money and frustration. Each system has specific requirements, but they all share the same basic infrastructure.
WiFi infrastructure planning starts with strategic access point placement during the cable design phase. You’ll need adequate PoE capacity to power wireless equipment, especially with newer WiFi 6E and future standards that require more power. Don’t forget to account for dead zones in buildings with brick walls or metal construction—these areas might need additional access points or specialized antenna placement.
VoIP phone systems have largely replaced traditional landlines, and modern phones use standard ethernet cables for both data and power. Plan for PoE+ power requirements since advanced phones with color displays and video capabilities need more power than basic models. Include backup power considerations for critical communications—your phones should keep working even during power outages.
Security system integration has evolved dramatically. Most CCTV cameras now use IP connections over ethernet rather than dedicated coax cables. Access control systems for doors and gates need network connectivity for remote management and monitoring. Plan cable pathways to reach door and window sensors, and consider how security monitoring and alarm systems will integrate with your network.
IoT and building automation represent the fastest-growing category of connected devices. Smart lighting controls, HVAC sensors, space utilization monitors, and environmental controls all benefit from structured cabling connections. While some IoT devices use wireless connections, the most reliable and secure installations use wired connections wherever possible.
The key is designing pathways and capacity for technologies you might not implement immediately. Installing extra conduit and cable runs during initial construction costs a fraction of what retrofitting requires later. Your Office Cabling system should be ready for the smart building technologies your business will adopt over the next decade.
Installation & Management Best Practices (Even for Non-Pros)
While we strongly recommend professional installation for Office Cabling systems, understanding best practices helps you oversee projects and maintain systems effectively.
More info about Network Cable Installations provides detailed guidance on professional installation standards and processes.
Step-by-Step “Pro” Install Checklist
Pre-Installation Planning:
1. Site Survey: Map building layout, identify cable pathways, and locate potential obstacles
2. Pathway Design: Plan routes through walls, ceilings, and floors while maintaining proper separation from electrical systems
3. Equipment Placement: Determine locations for telecommunications rooms, equipment racks, and patch panels
4. Pull Planning: Organize cable installation to minimize disruption and maximize efficiency
Installation Process:
1. Pathway Preparation: Install cable trays, conduits, and support structures
2. Cable Pulling: Run cables following planned routes with proper bend radius and support
3. Termination: Connect cables to jacks, patch panels, and equipment following manufacturer specifications
4. Testing: Certify each cable run using professional testing equipment
5. Documentation: Create detailed records of cable locations, connections, and test results
Quality Control:
– Maintain minimum bend radius (typically 4x cable diameter)
– Keep data cables at least 12 inches from electrical power lines
– Use proper cable support every 4-6 feet
– Follow manufacturer torque specifications for connections
Cable Management, Labeling & Documentation Hacks
Proper cable management isn’t just about appearance—it directly impacts system performance, maintenance efficiency, and troubleshooting speed. Research shows that proper cable management systems can reduce the time and costs associated with patch cord documentation management by up to 60%.
Labeling Best Practices:
– Use clear, wrap-around labels at every connection point
– Implement consistent naming conventions (Building-Floor-Room-Port)
– Apply labels before installation when possible
– Consider barcode or QR code systems for large installations
Color Coding Systems:
– Assign colors by function (blue for data, red for phones, yellow for security)
– Use consistent colors throughout the installation
– Document color schemes for future reference
– Consider colorblind-friendly schemes
Documentation Requirements:
– Create as-built drawings showing actual cable routes
– Maintain spreadsheets linking cable numbers to locations
– Include test results and certification data
– Store documentation both physically and digitally
Modern Management Tools:
– Cable management software with smartphone apps
– Bluetooth-enabled handheld scanners for cable tracing
– Digital test reports automatically linked to cable records
– Cloud-based documentation accessible to authorized personnel
Maintenance Schedule & When to Re-Certify
A well-installed Office Cabling system should last 10-15 years, but regular maintenance ensures optimal performance throughout its lifecycle.
Annual Maintenance Tasks:
– Visual inspection of cable pathways and connections
– Cleaning of equipment room air filters and cable management
– Verification of cable labeling and documentation accuracy
– Testing of critical network links and patch panel connections
5-Year Assessment:
– Performance testing of all cable runs
– Evaluation of capacity vs. current usage
– Review of technology changes and upgrade requirements
– Update of documentation and as-built drawings
10-15 Year Replacement Planning:
– Comprehensive system evaluation
– Technology roadmap assessment
– Budget planning for major upgrades
– Evaluation of new standards and capabilities
Signs requiring immediate attention:
– Frequent network disconnections or slow performance
– Physical damage to cables or connectors
– Changes in building use or occupancy
– New technology requirements exceeding current capabilities
Troubleshooting & Upgrade Timelines
Even the best Office Cabling systems can develop hiccups over time. The good news? Most problems have straightforward solutions, and knowing when to upgrade versus when to repair can save you significant time and money.

Think of network troubleshooting like detective work. The symptoms tell a story, and with the right tools and knowledge, you can usually track down the culprit quickly. Professional cable testers can identify problems in minutes that might take hours to find through trial and error.
Common warning signs include slow file transfers, dropped video calls, intermittent disconnections, and complete connection failures. While these symptoms can be frustrating, they’re usually caused by relatively simple issues like damaged patch cords, loose connections, or physical cable damage.
More info about The Benefits of Upgrading Your Business Cabling Infrastructure explains when repairs make sense versus when it’s time for a complete system refresh.
Common Office Cabling Problems & Quick Fixes
Slow network performance often feels like your internet connection is having a bad day, but the problem frequently lies in your Office Cabling. When file transfers crawl and video calls stutter, start by checking your patch cords. These short cables connecting devices to wall outlets take the most abuse and fail more often than the permanent cabling.
Look for kinked or overstretched cables first. I’ve seen cables that looked fine from a distance but had tiny kinks that reduced performance by 50%. Replace any questionable patch cords—they’re inexpensive and often solve performance problems immediately.
Intermittent disconnections are particularly maddening because they’re hard to predict and reproduce. These usually stem from loose connections at wall plates or patch panels. The solution is often as simple as unplugging and firmly reconnecting cables. If problems persist, the termination itself may need professional attention.
Complete connection failure at specific outlets requires systematic testing. Professional cable testers can quickly identify whether the problem lies in the patch cord, wall jack, horizontal cable, or patch panel connection. Don’t assume the cable itself is damaged—termination problems are more common and easier to fix.
Poor WiFi performance often traces back to cabling issues with access points. Insufficient Power over Ethernet can cause access points to operate at reduced power, creating dead zones. Check that your PoE switches provide adequate power for your wireless equipment’s full capabilities.
Physical damage from furniture, construction work, or even rodents requires immediate attention. Damaged cables can create safety hazards and network instability. When you spot physical damage, mark the cable clearly and arrange for professional replacement.
When Your Office Cabling Needs a Full Replacement
Sometimes repair isn’t the right answer. Technology obsolescence is the most common trigger for complete Office Cabling replacement. If your business needs 10 Gbps speeds but you have Cat5e cables, upgrading the equipment won’t help—the cables simply can’t handle the bandwidth.
Business growth spurts often overwhelm existing cabling systems. When you’re adding dozens of new employees or expanding into additional floors, it’s usually more cost-effective to design a new system than to patch onto an old one. This is especially true if your current system lacks proper documentation or wasn’t professionally installed initially.
Persistent performance problems that resist troubleshooting efforts often indicate systemic issues. If you’re constantly replacing patch cords, dealing with intermittent failures, or can’t achieve rated speeds despite new equipment, the underlying infrastructure may have reached its useful life.
Compliance requirements can force upgrades even when systems still function. Building code changes might require updated fire ratings, industry standards could mandate specific cable categories, or security requirements might necessitate shielded cables. These aren’t optional—they’re necessary for legal operation.
ROI analysis should guide your decision. When annual maintenance costs approach 20-30% of replacement costs, or when productivity losses from network problems become significant, replacement typically makes financial sense. Modern systems also offer energy savings that can offset upgrade costs over time.
Most businesses should plan for major upgrades every 10-15 years, with minor updates every 5-7 years to accommodate new technologies. However, rapidly growing companies or those in technology-intensive industries may need more frequent refreshes to stay competitive.
The key is planning ahead rather than waiting for crisis. A well-timed upgrade during slow business periods costs less and causes minimal disruption compared to emergency replacements when systems fail completely.
Frequently Asked Questions about Office Cabling
Let’s tackle the three questions I hear most often from business owners considering new Office Cabling systems. These answers come from thirty years of installing networks across New England, so I’ve seen what works (and what doesn’t) in real-world business environments.
How often should office cabling be assessed or upgraded?
Here’s the honest answer: it depends on how your business is growing and changing. Office Cabling systems are built to last, but they’re not “install and forget” infrastructure.
For most businesses, I recommend annual visual inspections where you or your IT team walks through and looks for obvious problems—damaged cables, overloaded patch panels, or equipment running unusually hot. These quick checks catch small issues before they become expensive emergencies.
Every five years, you’ll want a more thorough assessment. This means testing cable performance, reviewing your current usage against system capacity, and honestly evaluating whether your infrastructure still matches your business needs. Technology changes fast, and what seemed like overkill five years ago might be limiting you today.
The big decision point usually comes at 10-15 years. A well-installed system can absolutely last this long, but you’ll likely face a choice: invest in a major upgrade or continue maintaining an increasingly outdated system. Most of my clients find that upgrading at this point saves money compared to constant patches and workarounds.
Business growth accelerates everything. If you’ve doubled your staff, moved to a new building, or adopted bandwidth-hungry applications like video conferencing, you might need upgrades much sooner. The key is planning ahead rather than waiting for your network to become a bottleneck.
What certifications should my installer provide?
This is where many business owners get taken advantage of, so I’m glad you’re asking. Not all cable installers are created equal, and the certifications matter more than you might think.
Your installer should have BICSI credentials—that’s the Building Industry Consulting Service International, which sets standards for our industry. Look for RCDD (Registered Communications Distribution Designer) certification for complex projects. These aren’t just fancy letters; they represent real training and ongoing education requirements.
Manufacturer certifications are equally important. If your installer is working with specific cable brands or equipment, they should be factory-trained and certified on those products. This ensures they understand the nuances and requirements for proper installation.
Don’t forget about licensing requirements. Low-voltage electrical work requires proper licensing in most areas, and your installer should carry appropriate insurance and bonding.
After installation, you should receive comprehensive certification documentation. This includes performance test results for every single cable run, showing that each connection meets or exceeds the rated specifications. We also provide compliance documentation proving the installation follows TIA/EIA standards and local building codes.
The documentation package should include as-built drawings showing where cables actually run (not just where they were planned), a complete cable schedule, and warranty information covering both materials and workmanship. At AccuTech Communications, we treat this documentation as seriously as the installation itself—you’ll need it for future maintenance and upgrades.
How does Office Cabling support future technologies like 8K video and next-gen WiFi?
This question gets to the heart of why proper Office Cabling design matters so much. The infrastructure you install today needs to support technologies that don’t even exist yet.
8K video is already here, and it’s hungry for bandwidth—about 100 Mbps per stream. That might sound like a lot, but properly installed Cat6a cables can handle multiple 8K streams without breaking a sweat. The real magic happens when you have fiber optic backbones providing virtually unlimited capacity between network closets.
WiFi 7 and future wireless standards present interesting challenges. Each generation of wireless access points needs more power and higher-capacity connections to your wired network. The wireless speeds keep increasing, which means the wired infrastructure supporting those access points becomes even more critical.
Here’s what I tell my clients: design for what you need today, but install infrastructure that can handle much more. Use Cat6a instead of Cat6, even if you don’t need the extra capacity right now. Install fiber optic backbones even if your current equipment doesn’t require them. Plan for more PoE power than you think you’ll need.
Emerging technologies like augmented reality, advanced IoT sensors, and smart building systems all depend on reliable, high-performance cabling infrastructure. Electric vehicle charging, advanced security systems, and technologies we haven’t imagined yet will all connect to your network somehow.
The beautiful thing about structured cabling is that good infrastructure is incredibly adaptable. The Cat6a cables we install today will support network speeds that seemed impossible just a few years ago. Fiber optic systems have capacity that far exceeds anything most businesses will need in the foreseeable future.
When we design your Office Cabling system, we’re not just solving today’s problems—we’re building a foundation that will support your business for the next decade and beyond.
Conclusion
Building a professional Office Cabling system isn’t just about connecting devices—it’s about creating the foundation that keeps your business running smoothly for years to come. Think of it as the invisible infrastructure that makes everything else possible, from simple email to complex video conferences and smart building controls.
The journey we’ve covered—from understanding cable types to planning for future technologies—might seem complex at first glance. But here’s the thing: you don’t need to become a cabling expert overnight. What matters is understanding enough to make smart decisions and work effectively with qualified professionals.
Future-proof planning protects your investment and prevents the headaches that come with outdated systems. When you design for tomorrow’s needs today, you’re saving yourself from expensive emergency upgrades and frustrating downtime. A properly installed structured cabling system becomes your single source of truth for all building communications—data, voice, security, and smart building controls all working together seamlessly.
Reduced downtime is perhaps the most immediate benefit you’ll notice. No more hunting through tangles of unlabeled cables when something goes wrong. No more wondering if that connection failure is a cable problem or an equipment issue. Professional installation with proper testing and documentation means problems get solved quickly, keeping your team productive.
Investment protection extends far beyond the cables themselves. When your infrastructure can adapt to new technologies without major overhauls, you’re protecting every piece of equipment that connects to it. Your phone system, security cameras, WiFi access points, and future technologies we haven’t imagined yet—they all benefit from a solid foundation.
At AccuTech Communications, we’ve been helping businesses across Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Rhode Island build these foundations since 1993. We’ve seen companies grow from small startups to major enterprises, all supported by the same well-designed Office Cabling systems we installed years earlier. That’s the power of doing it right the first time.
Your cabling infrastructure should be something you set up once and then forget about—until you need to add something new or make a change. When that happens, a properly designed system makes those changes quick and painless instead of disruptive and expensive.
The technology landscape will keep evolving. New devices, faster speeds, smarter buildings—they’re all coming. But with the right foundation in place, you’ll be ready for whatever comes next. Your business will adapt and grow while your infrastructure quietly does its job, day after day, year after year.
More info about Network Cabling Installation to start building your reliable, future-ready network foundation with professional guidance every step of the way.

