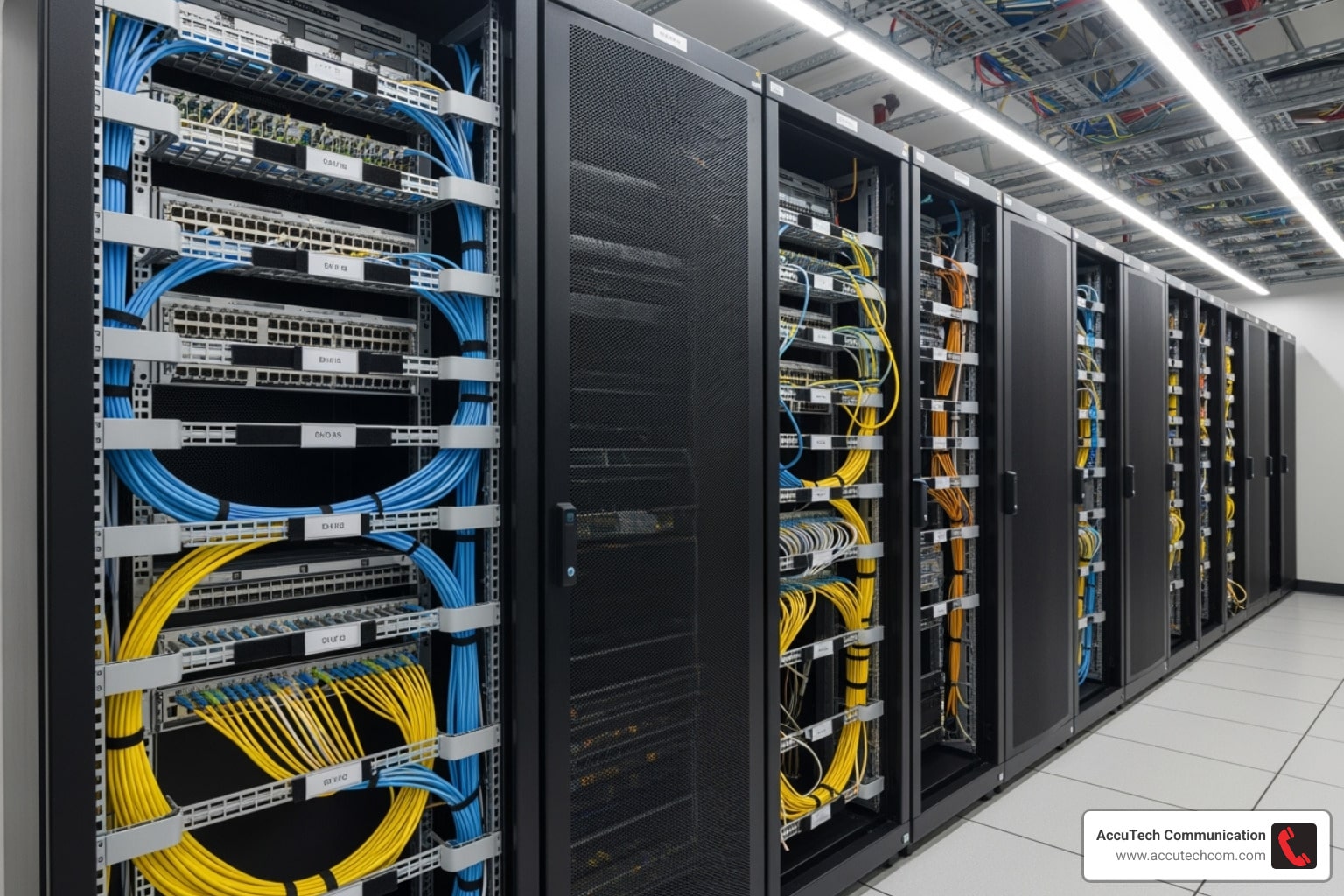
Data cabling installation: Smart Solutions 2025
Why Commercial Data Cabling Installation Forms Your Network Foundation
Data cabling installation is the process of creating a structured network of cables throughout a commercial building to connect computers, phones, security systems, and other devices. Here’s a brief overview:
Key Components:
- Structured cabling system – An organized network of cables following industry standards.
- Cable types – Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6A, and fiber optic cables for different speed requirements.
- Professional installation – Certified technicians ensure proper termination and testing.
- Planning phase – Includes a site survey, cable routing, and future capacity planning.
Typical Project Timeline:
- Small offices (under 1,000 sq ft): 3+ days
- Medium offices (5,000-10,000 sq ft): 1-2 weeks
- Large facilities (20,000+ sq ft): 4+ weeks
Your business network is its central nervous system. Poorly installed cabling leads to unreliable connections, slow data transfer, and costly downtime. Modern businesses rely on structured cabling for everything from internet access to VoIP systems and security cameras. A well-designed system lasts 15-20 years and adapts to evolving technology.
I’m Corin Dolan, owner of AccuTech Communications. Since 1993, we’ve helped businesses in Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Rhode Island build reliable network infrastructures. My experience shows that a solid data cabling installation prevents future headaches and supports long-term growth.
The Foundation: Understanding Structured Cabling and Its Components
Structured cabling is a comprehensive, standardized telecommunications infrastructure that supports all your business communications, from computers and phones to security cameras and Wi-Fi access points. Instead of a tangled mess, it creates an organized system that is scalable, reduces downtime, and simplifies network management.
This system operates on low-voltage wiring (50 volts or less), which is distinct from high-voltage electrical wiring. Low-voltage systems require specialized knowledge for installation and safety, covering not just data but also security, audio/visual, and smart building technologies.

Key Components of a Structured Cabling System
Professional data cabling installation follows Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) standards, which define six key components:
- Entrance Facility: Where external service provider cables enter your building and connect to your internal network.
- Equipment Room: A centralized space housing critical network equipment like servers, switches, and routers.
- Telecommunications Room (TR): Strategically placed closets (or wiring closets) that house patch panels and switches to connect the backbone to horizontal cabling for specific floors or areas.
- Backbone Cabling (Vertical Cabling): High-capacity cables (often fiber optic) that connect the equipment room, TRs, and entrance facility.
- Horizontal Cabling: Cables running from TRs to individual work area outlets.
- Work Area: The final connection point, including wall plates and patch cords, where users connect their devices.
Two other vital components are patch panels, which centralize cable terminations for easy network changes, and keystone jacks, the modular connectors in wall plates and patch panels that provide a standardized interface for devices.
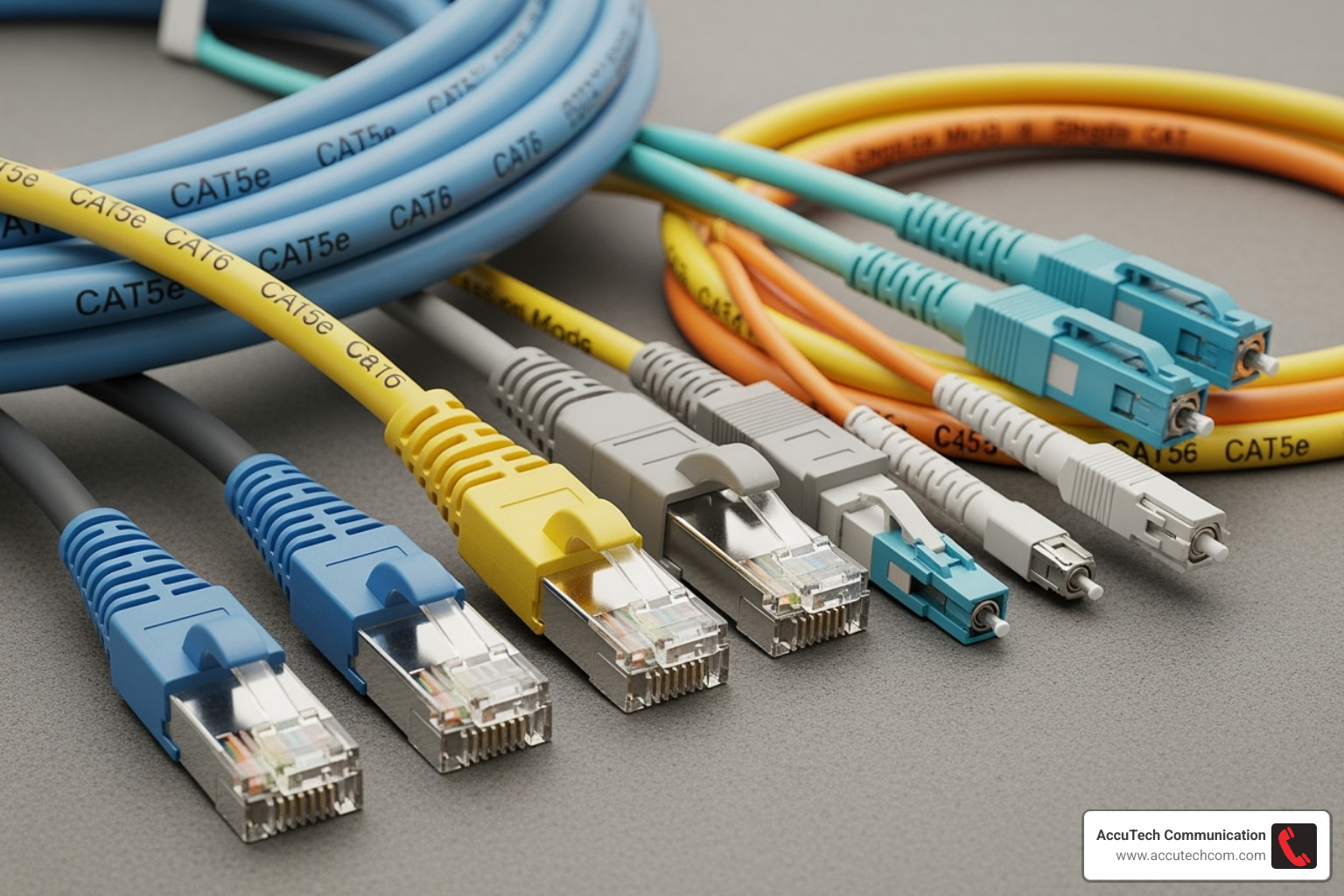
Types of Network Cables and Their Applications
- Ethernet Cables: The most common network cables, using twisted pairs of copper wires to reduce interference. They connect devices like computers, printers, and VoIP phones. For a deeper dive, you can read what is an Ethernet cable. Conductors can be solid (for permanent in-wall runs) or stranded (for flexible patch cords). Cables are available as Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP), the common choice for offices, or Shielded Twisted Pair (STP), which offers extra protection against electrical noise in industrial environments.
- Fiber Optic Cables: Transmit data using light, offering much higher bandwidth and longer distance capabilities than copper. Fiber is ideal for backbone cabling, connecting buildings, and high-speed data centers. You can find more info about fiber optic cabling services on our site.
- Coaxial Cables: Less common today, but still used for cable television, broadband internet, and some video surveillance systems.
A Closer Look at Ethernet Cable Categories
Choosing the right Ethernet category ensures your network meets current and future needs.
- Cat5e: Supports 1 Gbps speeds (100 MHz bandwidth). Sufficient for basic office needs and VoIP, but now considered outdated for new installations.
- Cat6: Supports 1 Gbps over 100 meters and up to 10 Gbps over shorter distances (55m), with 250 MHz bandwidth. Ideal for modern Gigabit Ethernet networks.
- Cat6A: Delivers 10 Gbps speeds over the full 100-meter distance (500 MHz bandwidth). The standard for data centers and future-proofing large networks.
- Cat8: Provides 25-40 Gbps speeds (2000 MHz bandwidth) over short distances (30m). Used primarily in data centers.
Note: “Cat6E” is not a recognized standard and should be avoided.
Cable jacket ratings indicate fire safety for different installation environments: CM (General Purpose), CMR (Riser, for vertical runs between floors), CMP (Plenum, for air-handling spaces), and CMX (Residential/Outdoor).
Planning Your Commercial Data Cabling Installation
Planning your data cabling installation is like creating a blueprint for a building’s foundation. A solid plan impacts your business operations for the next 15-20 years. Key planning considerations include:
- Future-proofing: Install extra capacity now to avoid costly upgrades later.
- Facility Size and Layout: A site survey is essential to map efficient cable routes and identify obstacles like HVAC systems or structural elements.
- Scalability: Design the system to accommodate future growth in personnel, devices, and technology.
- Drops Per Room: While standards suggest two drops per work area, modern offices often need more. Conference rooms may need six or more for presentation equipment and guest access. Plan for both current and future needs in each space.
- Bandwidth Requirements: Assess your specific applications (e.g., video conferencing, cloud services, large file transfers) to select the right cable category and prevent network bottlenecks.
- Budgeting: Look beyond the initial cost and consider the long-term value of preventing downtime, reducing service calls, and ensuring reliable performance.

Key Steps in the Data Cabling Installation Process
A quality installation follows a proven sequence:
- Site Survey and System Design: We conduct a thorough walkthrough to understand your workflow, identify obstacles, and design a network that supports your operations.
- Cable Pulling and Routing: Technicians route cables through planned paths, ensuring proper separation from electrical lines to prevent interference.
- Termination: Each cable is precisely terminated with the correct connector. This step is critical, as poor termination is a primary cause of network failure.
- Labeling: Every cable is clearly marked at both ends, creating a clear map of your network for easy troubleshooting and management.
- Testing and Certification: Using professional certification equipment, we test every cable to verify it meets TIA performance standards, providing you with detailed reports.
- Documentation: You receive complete records, including floor plans and test results, which serve as a roadmap for future network modifications.
Best Practices for a Flawless Installation
- Adhere to TIA/EIA Standards: Guarantees system performance, reliability, and compatibility.
- Maintain Bend Radius: Prevents damage to internal conductors by avoiding overly tight bends.
- Separate Data and Power Cables: Avoids signal disruption from electromagnetic interference.
- Use Proper Cable Management: Employs trays and raceways to organize cables, improve airflow, and simplify maintenance.
- Incorporate Service Loops: Leaves slack cable at termination points for easier future moves, adds, and changes.
- Perform Comprehensive Testing: Identifies and corrects any faulty connections before the project is completed.
When is the Right Time to Upgrade Your Cabling?
Strategically timing your data cabling installation can save money and minimize disruption. The best times to upgrade are during:
- New Construction: Install cabling while walls are open for cleaner, lower-cost results.
- Major Renovations: Upgrade your network infrastructure when you are already opening walls for other projects.
- Technology Upgrades: A move to VoIP or new servers may require more bandwidth than your current cabling can provide.
- Persistent Network Issues: If slowdowns and dropped connections are common, outdated cabling is often the culprit.
- Business Expansion: Ensure your network can support more users and devices without performance issues.
Decoding the Costs and ROI of Professional Installation
When considering a data cabling installation, it’s crucial to look beyond the initial price and evaluate the long-term return on investment (ROI). A quality installation is an asset that pays dividends for years.
Key cost factors include the cable type (e.g., Cat6A vs. fiber optic), the number of drops, regional labor rates, and the complexity of the facility. Historic buildings or complex layouts can increase installation time and cost.
However, the ROI is significant. A professionally installed system delivers:
- Reduced Downtime: Reliable connections prevent lost productivity and revenue.
- Longevity: A structured cabling system can last 15-20 years, spreading the investment over two decades.
- Lower Maintenance Costs: Organized, labeled systems make troubleshooting faster and cheaper than navigating a “spaghetti” mess of wires.
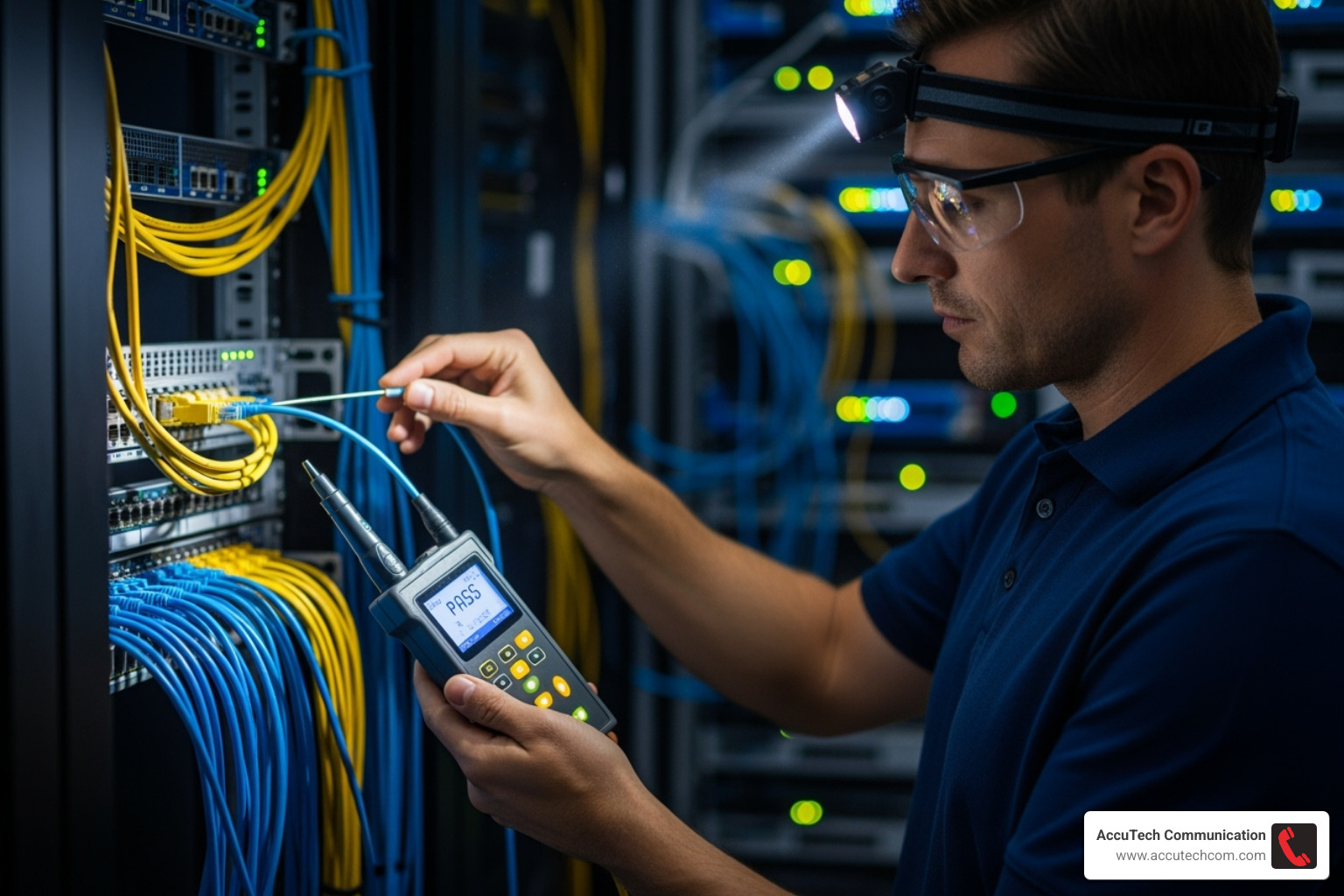

Why Professional Data Cabling Installation is a Smart Investment
Attempting a DIY approach or hiring a general electrician for data cabling installation often leads to poor performance. It’s a specialized field distinct from high-voltage electrical work. A professional installer provides:
- Expertise and Certification: Technicians understand data transmission science, termination techniques, and performance standards.
- Proper Tools: We use expensive certification testers to verify that every cable meets performance specifications, something basic testers cannot do.
- Adherence to Codes and Standards: We follow TIA/EIA standards and local building codes to ensure safety, reliability, and scalability.
- Warranty and Support: We stand behind our work with comprehensive warranties, giving you peace of mind. Explore our structured cabling services to learn more.
- Safety and Efficiency: Professionals work safely around existing systems and complete projects with minimal disruption to your business.
Understanding Project Costs and Timelines
Project scope varies based on facility size and complexity. General timelines are:
- Small Offices (under 1,000 sq ft): Typically take 3+ days.
- Medium-Sized Offices (5,000-10,000 sq ft): Usually require 1-2 weeks, often involving multiple wiring closets.
- Large Facilities (20,000+ sq ft): Can take 4+ weeks, especially with multiple floors and a sophisticated backbone.
- Multi-Floor or Campus Environments: These complex projects can span several months.
To get an accurate quote, an on-site assessment is essential. There is no substitute for walking through your facility to understand its unique challenges. Providing detailed information about your user count, device types, and growth plans helps us design a system that will serve you well for years.
Frequently Asked Questions about Data Cabling
Over three decades, we’ve answered thousands of questions about data cabling installation. Here are the most common ones.
What is the difference between structured cabling and regular cabling?
Structured cabling is a standardized, organized system designed for long-term reliability and scalability. It follows industry standards (TIA/EIA) to support voice, data, and video. Every connection is planned and documented.
In contrast, regular or point-to-point cabling is an ad-hoc approach that results in a disorganized, unreliable mess of wires. This “cable spaghetti” is difficult to manage, troubleshoot, and upgrade, leading to more downtime and higher maintenance costs.
How many network cables should be run to each office or workstation?
While the TIA standard suggests a minimum of two drops per work area, modern needs often require more. A typical user may need connections for a computer, a VoIP phone, and a printer. Conference rooms require even more for presentation gear and guest access.
Running extra cables during the initial data cabling installation is far more cost-effective than adding them later. It’s always better to have a drop you don’t need than to need a drop you don’t have.
Can an electrician install data cables?
While electricians are skilled in high-voltage work, data cabling installation is a specialized low-voltage field that requires different expertise. Data cabling is about signal integrity, not just connectivity.
Certified low-voltage technicians understand how to prevent signal degradation, crosstalk, and other issues that degrade network performance. We use specialized certification testers—which cost thousands of dollars—to verify that every cable meets strict performance standards for speed and reliability. This equipment and expertise are crucial for a high-performance network and are not typically part of an electrician’s toolkit. A professional installation comes with certified test results and a warranty, ensuring your network will support your business for years.
Conclusion
Your business network is the invisible foundation of your daily operations. A professional data cabling installation works seamlessly in the background, while a poor one causes constant headaches and disrupts productivity. A properly designed structured cabling system provides consistent performance, reliability, and scalability for future growth.
The long-term value is clear. A well-installed system can serve your business for 15-20 years, making it a sound investment that minimizes downtime and reduces ongoing maintenance costs. Compared to the expense of constant troubleshooting and lost productivity, the choice is simple.
Since 1993, AccuTech Communications has been a trusted partner for businesses across Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Rhode Island. We’ve seen technology evolve, but the need for a solid, professionally installed network foundation has never changed. Our certified technicians don’t just install cables—they build the infrastructure that powers your success.
Your business deserves a network that works as hard as you do. Ready to build a foundation that lasts? Contact a professional network cabling company for a consultation and learn how our three decades of experience can transform your business communications.

