Business network setup: Ultimate 5 Steps to Success
Why Your Business Network Setup Matters More Than Ever
A professional business network setup is the foundation of any modern organization. Your network infrastructure directly impacts productivity, security, and your ability to serve clients. A well-designed network connects computers, printers, servers, and phones, enabling file sharing, video conferencing, and secure internet access.
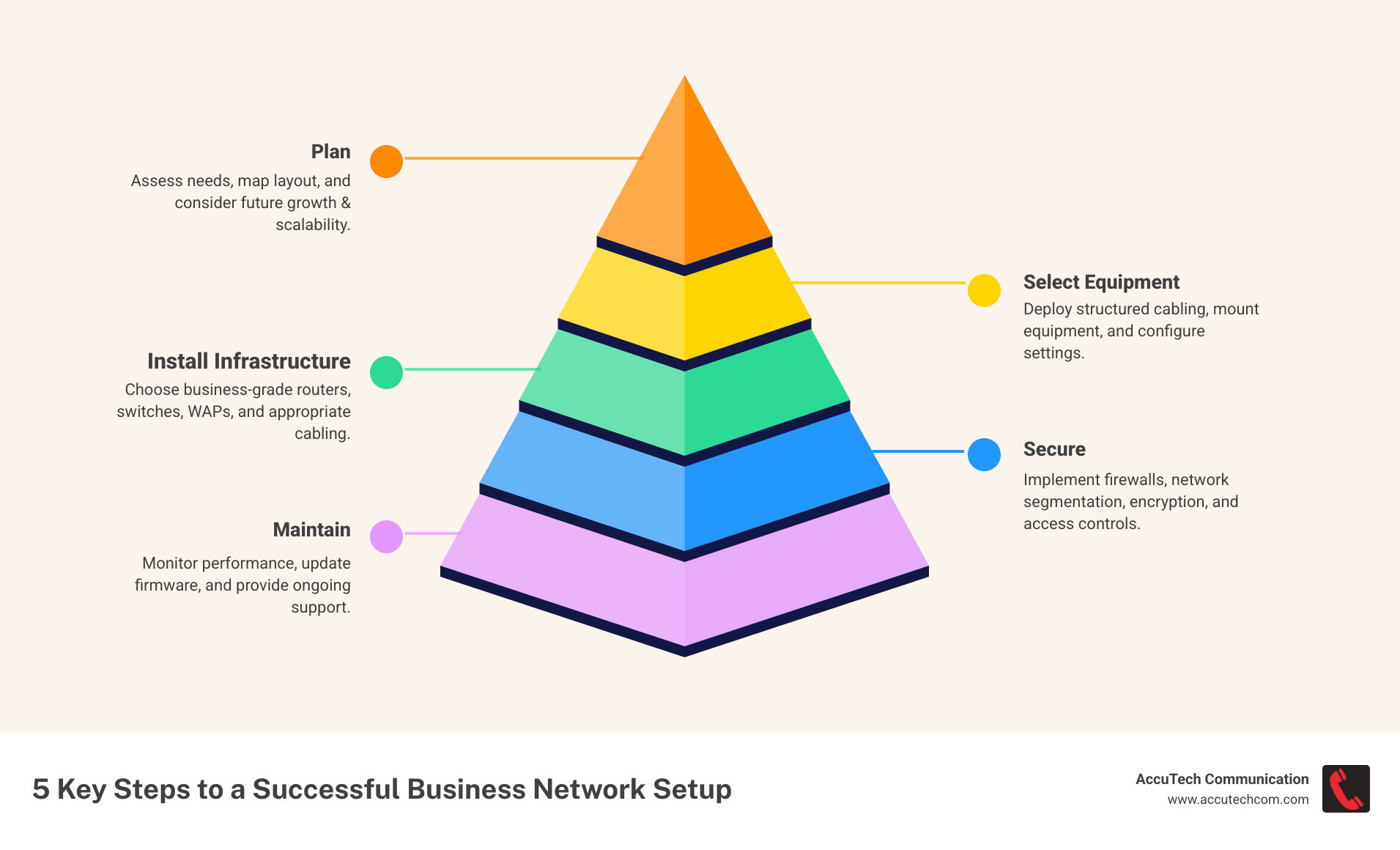
A proper setup involves five key steps:
- Planning: Assessing current needs and future growth.
- Selecting Equipment: Choosing business-grade hardware.
- Installing Infrastructure: Deploying cabling and configuring devices.
- Securing: Implementing firewalls, VPNs, and other protections.
- Maintaining: Monitoring performance and updating systems.
The stakes are high. Downtime from network failures costs businesses an average of $5,600 per minute. Outdated or consumer-grade equipment creates security risks and hurts productivity, lacking the reliability and scalability businesses require.
I’m Corin Dolan, owner of AccuTech Communications. Since 1993, my team has designed and implemented business network setup solutions for companies across Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Rhode Island, building reliable infrastructure that supports their success.
Similar topics to Business network setup:
Step 1: Planning and Designing Your Network
The difference between a reliable network and a problematic one lies in planning. A thoughtful business network setup requires a blueprint, just like building a house. This phase maps out your business needs for today and tomorrow.
We start by assessing your requirements: How many users and devices (desktops, laptops, VoIP phones, security cameras) will be on the network? We also analyze your physical space to determine equipment placement and connectivity, factoring in future renovations or expansions. Planning for growth now is far more cost-effective than overhauling your network later. We also build in redundancy and failover options to prevent a single point of failure from halting your operations.
A key deliverable is a network map—a visual blueprint showing how devices connect and data flows. This document is invaluable for troubleshooting and future upgrades.
Planning Your Business Network Setup for Success
A successful plan considers your operational realities. Are you running bandwidth-heavy video conferences or using cloud applications that need fast, consistent internet? We look three to five years ahead, anticipating staff growth, new IP security cameras, or a cloud-based phone system.
Your physical infrastructure, built on quality Data Cabling Installation, is critical. The right cables support not just today’s speeds but tomorrow’s as well. We also help you decide between physical and cloud infrastructure. While some businesses need on-site servers for regulatory or performance reasons, others benefit from the flexibility of cloud-based systems. A hybrid approach, combining on-site systems with cloud services for backup and collaboration, is often the most practical solution.
Business-Grade vs. Consumer-Grade Equipment
While the lower price of consumer-grade networking equipment is tempting, it’s designed for home use, not for a business where downtime costs money. Business-grade equipment is the right choice for several key reasons:
- Reliability: Built with superior components and cooling, business-grade devices are designed for continuous 24/7 operation without failure.
- Security: They include advanced firewalls, intrusion detection, and VPN support to protect sensitive business and customer data from sophisticated threats.
- Scalability: Business equipment is designed to grow with you, supporting more users and devices without requiring a complete replacement.
- Performance: It handles higher traffic volumes and maintains faster speeds under load, ensuring smooth operation for large file transfers and video calls.
- Management: Remote monitoring, central configuration, and proactive alerts save significant time on IT administration.
When considering the total cost of ownership, business-grade equipment is more cost-effective. The higher upfront cost is offset by reduced downtime, better security, a longer lifespan, and easier management. For more context, see our page on Cabling and Networking. A proper business network setup with the right equipment supports your success rather than holding you back.
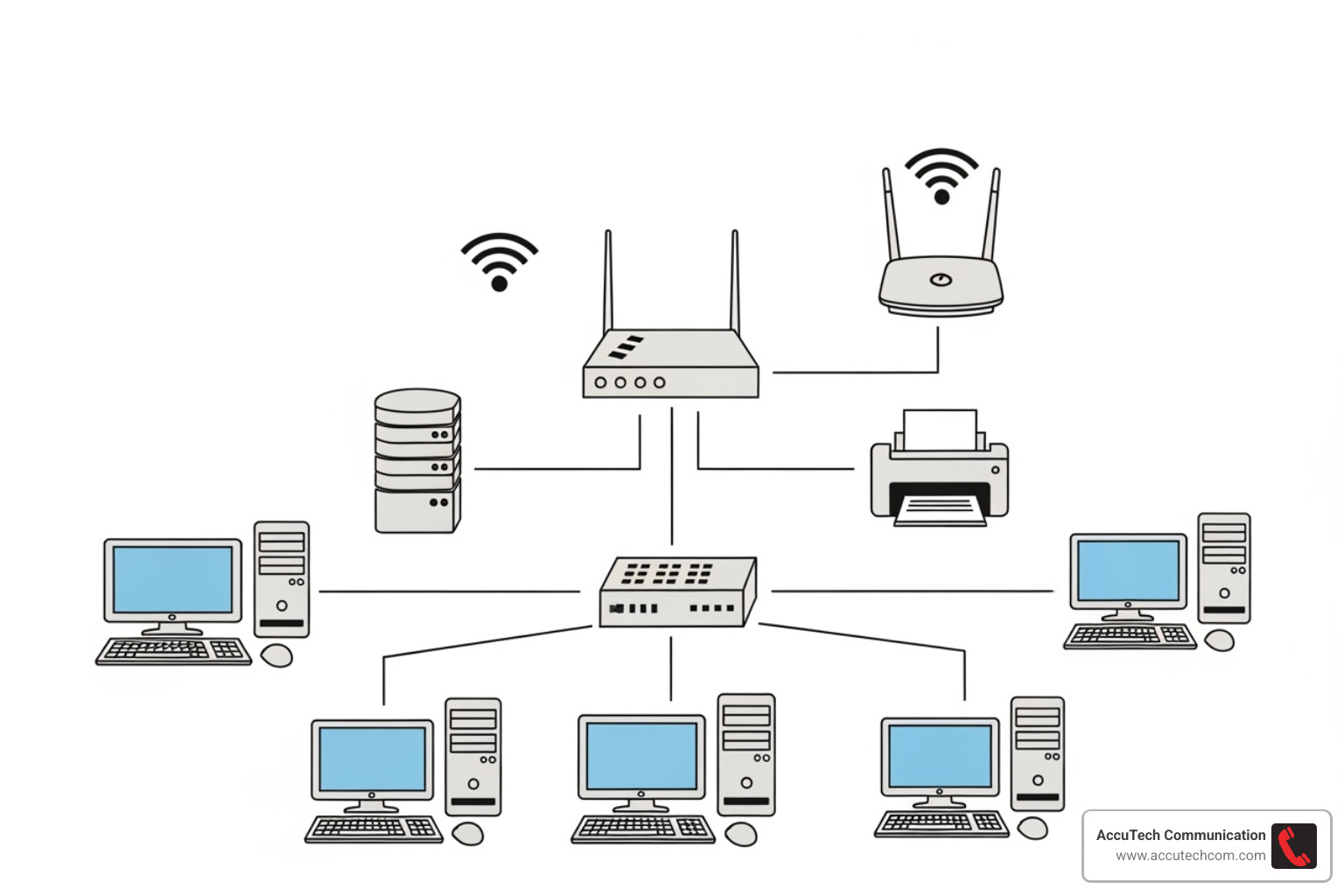
The Core Components of Your Business Network Setup
Your business network setup is a team of components working together. Understanding their roles is key to building a supportive system.
- Internet Service Provider (ISP) & Modem: Your ISP provides your connection to the outside world, and the modem translates that signal for your network.
- Router: The traffic cop of your network, directing data between your internal network and the internet. It’s your first line of defense.
- Network Switch: Connects internal devices like computers and printers, allowing them to communicate with each other.
- Firewall: A dedicated security device that monitors traffic and blocks unauthorized access and malware.
- Wireless Access Points (WAPs): Broadcast Wi-Fi signals throughout your office for wireless connectivity.
- Servers: Central hubs for storing data, running applications, and managing shared resources.

Router vs. Switch: Understanding the Difference
In a business network setup, routers and switches have distinct and vital roles. They are not interchangeable.
| Feature | Router | Switch |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Connects different networks (e.g., your office LAN to the Internet). | Connects devices within a single local network (LAN). |
| Traffic Direction | Directs data packets between networks, determining the best path. | Forwards data packets directly to the intended device on the same LAN. |
| Internet Access | Essential for providing internet access to your entire network. | Does not directly provide internet access. |
| Security Role | Acts as the first line of defense, often including firewall features. | Primarily for internal network communication, less focused on security. |
| Where it’s Necessary | Always needed to connect to the internet and isolate your internal network. | Needed when you have more wired devices than your router’s ports can handle, or to segment your internal network. |
In short, your router is the gateway to the internet, while the switch creates the internal network connecting your local devices. You always need a router for internet access; a switch is added to expand the number of available wired connections. This distinction is key to understanding What is an Example of Network Communication?.
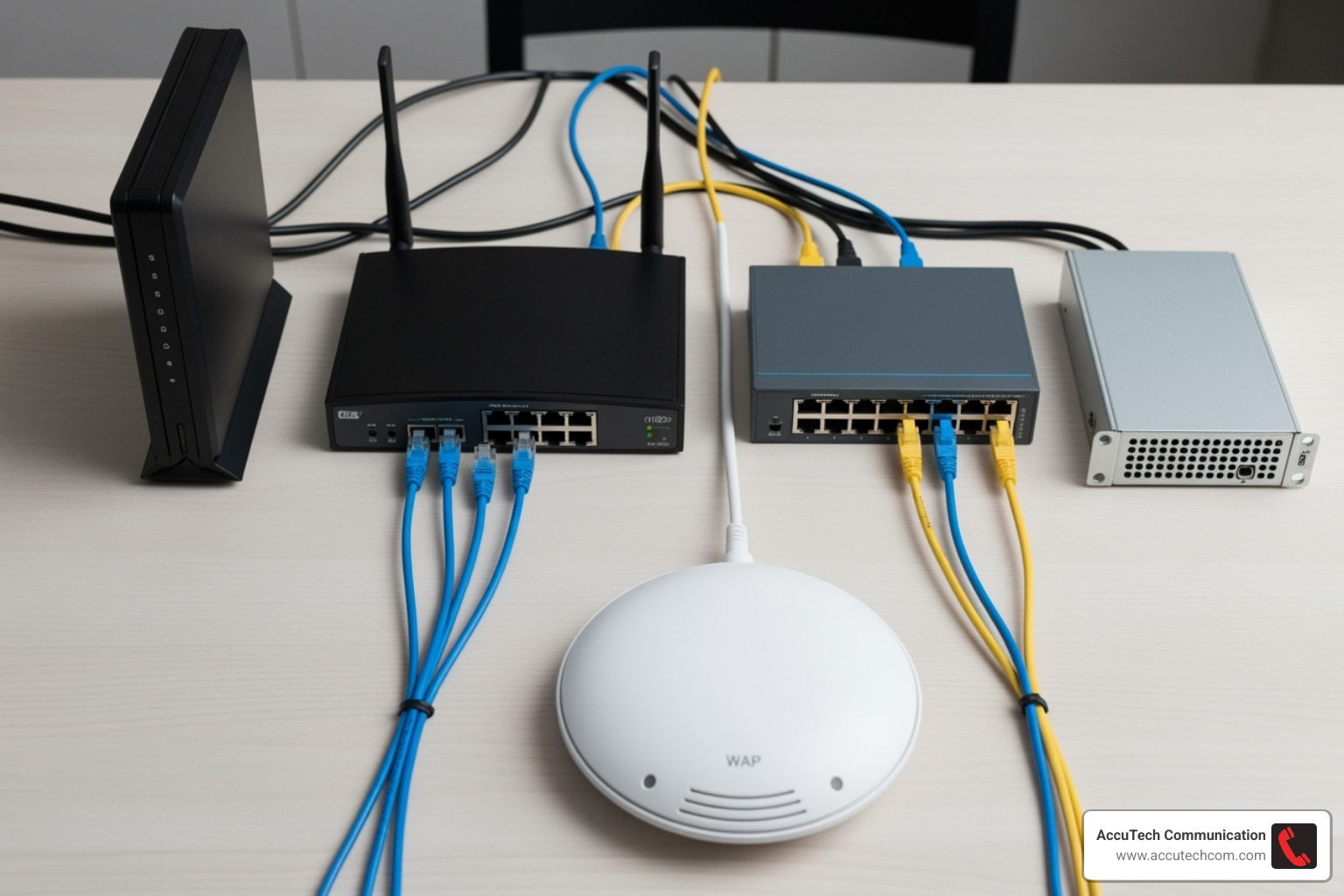
Choosing Your Hardware
Selecting the right hardware ensures your business network setup can meet today’s needs and grow for tomorrow.
- Router: Look for business-grade models with VPN support for secure remote access and Quality of Service (QoS) to prioritize critical traffic like VoIP calls.
- Switch: Choose based on the number of devices you need to connect (8, 16, 24, or 48 ports). Managed switches offer greater control and segmentation, while Power over Ethernet (PoE) support can power devices like phones and cameras through the network cable.
- Wireless: Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) is the current standard, offering faster speeds and better performance in crowded environments. Multiple access points are usually needed for full office coverage.
- Firewall: Ensure your security appliance has enough firewall throughput to inspect traffic without creating a bottleneck. Next-generation firewalls offer the best protection.
- Servers: If using on-site servers, choose based on their function, whether for basic file storage or high-performance applications.
All this hardware is connected by quality cabling. Understanding Network Cable Categories is crucial to ensure your equipment performs at its rated speed.
Step 2: Choosing Your Network Type: Wired, Wireless, or Hybrid?
A key decision in your business network setup is how devices will connect. The choice between wired, wireless, or a hybrid model impacts speed, security, and flexibility. There’s no single right answer; it depends on your business needs, office layout, and budget.

The Case for a Wired Network
Wired networks, using Ethernet cables, remain the gold standard for business-critical connections that demand top performance. Their main advantages are speed and stability. Wired connections offer consistently faster data transfer rates (Gigabit Ethernet is standard) and are immune to the interference that can affect Wi-Fi. From a security standpoint, a physical connection is inherently more secure, as it requires direct access to your cables.
Wired networks are ideal for stationary devices like desktops, servers, and printers. Professional Structured Cabling creates a clean, high-performing foundation. For new installations, we recommend at least CAT6 cabling, with CAT6a being a worthwhile investment for future-proofing for 10 Gigabit speeds.
The Flexibility of a Wireless Network
Wireless networks (Wi-Fi) offer the mobility and flexibility essential in modern offices. Employees can stay connected while moving between desks, conference rooms, or common areas. Deploying wireless access points can also be easier and less disruptive than running cables, especially in older buildings.
Wi-Fi simplifies guest access by allowing you to create a separate, secure network for visitors. Modern Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) technology has significantly improved wireless speed, capacity, and performance in crowded environments. However, wireless is generally slower than wired and can be affected by physical obstructions. For common issues, Microsoft’s guide on Fix Wi-Fi connection issues in Windows can be helpful.
The Hybrid Approach: Best of Both Worlds
Most businesses benefit from a hybrid network, which combines the strengths of both wired and wireless. This approach provides maximum reliability where it’s needed most, while preserving the flexibility that modern work demands.
In a hybrid business network setup, critical devices like servers, desktops, and VoIP phones use stable wired connections. Meanwhile, strategically placed wireless access points provide seamless coverage for laptops, tablets, and mobile devices. This allows your team to be productive anywhere in the office.
A key advantage of the hybrid model is the ability to segment traffic using VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks). This lets you prioritize critical applications, isolate guest traffic from internal systems, and add security layers for sensitive data. A solid Office Cabling backbone ensures all components integrate into a unified, powerful network.
Step 3: Installation, Security, and Management
With a plan and hardware selected, the next phase of your business network setup is execution. This involves physical installation, software configuration, and establishing ongoing security and management practices.
The physical installation includes running and terminating cables, mounting equipment like routers and switches in secure racks, and strategically placing wireless access points for optimal coverage. Proper cable management is crucial—a neat, labeled installation simplifies future troubleshooting and maintenance, a core principle of effective Data Center Infrastructure Management.
After the physical setup, we configure the software: assigning IP addresses, setting up firewall rules, and creating Wi-Fi networks. However, a network is not a “set it and forget it” system; it requires ongoing maintenance to remain secure and performant.
Securing Your Network
Network security is non-negotiable. A multi-layered approach is the best defense against modern threats.
- Firewall Implementation: A dedicated hardware firewall acts as your primary security guard, monitoring all traffic and blocking malicious activity. Next-generation firewalls offer advanced protection like intrusion prevention and content filtering.
- Network Segmentation: Using VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks), we divide your network into isolated segments. This contains potential breaches, for example, by keeping your guest Wi-Fi completely separate from your internal business systems.
- Secure Access: A VPN (Virtual Private Network) is essential for remote employees, creating an encrypted tunnel to safely access network resources. For wireless, WPA3 encryption is the current security standard.
- Essential Practices: Enforce the use of strong, unique passwords on all network devices and Wi-Fi networks. Perform regular firmware updates on all hardware to patch security vulnerabilities, scheduling them during off-hours to minimize disruption.
For more technical details, Microsoft’s guide to Set up your small business network – Windows Client | Microsoft Learn is a useful resource.
Leveraging Cloud Services and Redundancy
A modern business network setup integrates cloud services and redundancy for greater resilience.
Cloud-based management platforms allow for remote monitoring and troubleshooting of your network from anywhere. For disaster recovery, off-site cloud backups are essential to protect your data from physical events like fire or theft. Many businesses also adopt SaaS (e.g., Microsoft 365) and IaaS (cloud servers) to reduce on-premise hardware costs and improve scalability.
To ensure constant connectivity, failover internet connections from a secondary provider can automatically take over if your primary service goes down. An Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) provides battery backup during power outages, preventing data corruption and giving you time to shut down systems safely. For major moves, professional Server Relocation services minimize downtime.
Step 4: Budgeting and Future-Proofing Your Network
A successful business network setup requires smart financial planning. It’s crucial to look beyond initial hardware prices and consider the total cost of ownership (TCO). This includes installation, maintenance, security, and future upgrades. Investing in quality components and professional installation from the start leads to lower long-term costs by minimizing downtime and costly emergency fixes.
For a small business, the initial investment reflects the complexity, size, and security requirements of the network. Every dollar spent on proper infrastructure is an investment in productivity and growth. Our guide on Commercial Network Cable Installation Pricing provides more detailed insights.
Cost Breakdown for a Small Business Network Setup
Understanding where your investment goes helps in budgeting for your business network setup. The primary costs include:
- Network Hardware: The routers, switches, and wireless access points that form the core of your network.
- Structured Cabling Installation: The physical foundation of your network. Cutting corners here leads to performance issues later.
- Professional Labor and Configuration: Expert setup optimizes performance and security, saving you headaches down the road.
- Security Infrastructure: Essential firewalls and software to protect against data breaches.
- Ongoing Annual Costs: Budgets for maintenance, software licenses, and support to keep the network secure and performant.
Ensuring Network Scalability and Reliability
The best business network setup is one that grows with you. Planning for scalability from day one prevents expensive overhauls later.
- Choose Scalable Hardware: Select modular switches that allow you to add ports as needed and routers with enough processing power to handle future traffic increases.
- Plan for Future Cabling: Running extra cables during the initial installation is far cheaper than adding them later. This is especially true for Fiber Optic Installation, which offers immense bandwidth for future needs.
- Incorporate Redundancy: For critical components like routers and firewalls, redundant hardware can automatically take over in case of a failure, ensuring business continuity.
- Secure Strong SLAs: When choosing an internet provider, look for a Service Level Agreement (SLA) that guarantees uptime and support response times. This is your safety net for connectivity.
Frequently Asked Questions about Business Network Setup
What are the first steps to setting up a business network?
The first step in any business network setup is planning. Before buying any equipment, you must assess your needs: How many users and devices will be on the network? What critical applications (e.g., VoIP, cloud software) do you use? Based on this assessment, create a detailed network plan and a realistic budget that accounts for hardware, installation, and security. This initial planning is crucial for building a reliable and scalable network.
How much does it cost to set up a network for a small business?
The cost varies, but for a small business with 10-50 employees, the initial investment typically includes network hardware (routers, switches, access points), structured cabling installation, professional labor for configuration, and security appliances. Beyond the upfront costs, be sure to budget for ongoing annual expenses for maintenance, security updates, and support services to keep your network running smoothly and securely. A well-designed network is an investment that pays for itself through increased productivity and reduced downtime. For more detail, see our guide on Commercial Network Cable Installation Pricing.
Can I use a consumer-grade router for my small business?
While a consumer-grade router might work for a home office with one or two people, it is not recommended for a business with employees and sensitive data. Consumer equipment lacks the essential security features, reliability, and performance needed for a business environment. Business-grade equipment is engineered to run 24/7, offers advanced security like VPNs and robust firewalls, and is scalable to grow with your company. While the upfront cost is higher, the total cost of ownership is lower due to reduced downtime, better security, and a longer lifespan, making it the smarter investment for any professional business network setup.
Conclusion
Your business network setup is the digital backbone of your company. A well-designed network connects your team, protects your data, and keeps your operations running smoothly. When done right, it boosts efficiency and enables growth. When done poorly, it leads to dropped connections, security risks, and costly downtime.
Investing in a professional network—from planning and hardware selection to security and future-proofing—is an investment in your business’s success. It ensures your employees can work efficiently, your data remains secure, and your infrastructure can scale as you grow.
At AccuTech Communications, we’ve been helping businesses across Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Rhode Island build reliable, scalable networks since 1993. We understand the unique needs of different industries, from healthcare to manufacturing, and we are committed to delivering certified, reliable service at competitive prices.
Don’t let an inadequate network hold your business back. Whether you’re setting up a new office or upgrading an aging system, we’re here to help you build an infrastructure that works as hard as you do.
Ready to build a network that empowers your team and protects your business? Enhance Your Business with Expert Network Cabling in Massachusetts.

