How Far Can Fiber Optic Cable Run: Top Insights 2025
How far can fiber optic cable run? This question often pops up for businesses considering network upgrades, especially in sectors like healthcare, which require fast and dependable communication systems. For those seeking a quick answer, here’s the gist:
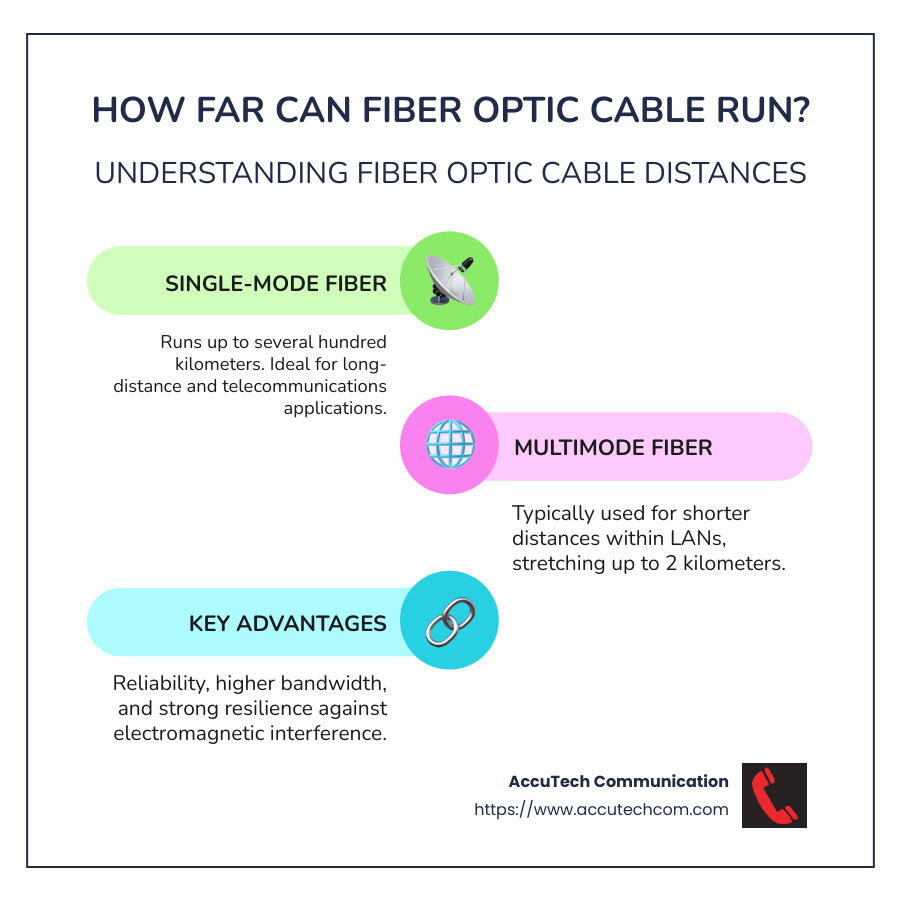
- Single-mode fiber optic cables can run up to several hundred kilometers, suitable for long-distance and telecommunications applications.
- Multimode fiber optic cables, on the other hand, are generally used for shorter distances, typically within local area networks (LANs), stretching up to 2 kilometers.
Opting for fiber optic cabling provides significant advantages. It’s not just about the distance. It’s about reliability, higher bandwidth, and stronger resilience against electromagnetic interference compared to traditional copper cabling. These features make fiber optics ideal for a wide array of industries and applications.
As someone who’s been deeply involved in this field, I’m Corin Dolan, and I’ve spent years helping businesses understand how far can fiber optic cable run. My expertise spans fiber optic deployment and solutions that cater to robust communication needs across Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Rhode Island.
How far can fiber optic cable run terms explained:
– how do fiber optic cables work
– types of fiber optic cable
– what are fiber optic cables used for
Understanding Fiber Optic Cable Types
Fiber optic cables come in different types, each serving unique purposes. Let’s break down the key types: single-mode fiber, multimode fiber, and G.652 fiber.
Single-Mode Fiber
Single-mode fiber is the go-to choice for long-distance applications. Its core is very thin, allowing light to travel straight down the fiber with minimal reflection. This makes it perfect for telecommunications networks that need to cover vast distances—up to several hundred kilometers.
Why is this important? Because when you’re running a network across cities or even countries, you need a cable that can handle the distance without losing signal strength. Single-mode fiber does just that.
Multimode Fiber
On the flip side, multimode fiber is designed for shorter distances. Its larger core allows multiple light signals to travel simultaneously, making it ideal for local area networks (LANs). These cables usually stretch up to 2 kilometers and are often used in office buildings or campuses.
The flexibility of multimode fiber makes it a favorite for setting up internal networks. It’s less expensive than single-mode and works great for shorter, high-speed connections.
G.652 Fiber
G.652 fiber is a subtype of single-mode fiber. It’s commonly used in telecommunications because of its low attenuation and dispersion. This means it can carry signals over long distances with minimal loss and distortion.
G.652 is often used in backbone networks that require high-speed data transfer across significant distances. It’s a versatile option for companies looking to future-proof their infrastructure.
Understanding these types helps in choosing the right fiber optic solution for your needs. Whether it’s single-mode for long hauls or multimode for short hops, each type has its strengths. And with G.652, you get a specialized option for robust data transmission.
Next, we’ll explore the factors that can affect the range of fiber optic cables, such as attenuation and dispersion.
How Far Can Fiber Optic Cable Run?
When it comes to how far can fiber optic cable run, the answer depends on several factors, including the type of fiber used and the technology applied. Let’s explore the specifics for single-mode and multimode fiber optic cables.
Single-Mode Fiber Optic Cable Distances
Single-mode fiber is designed for long-distance applications. Thanks to its thin core, it allows light to travel in a straight path, reducing the chances of signal loss. This makes it ideal for telecommunications networks that span across cities or even countries.
In terms of distance, single-mode fiber can easily cover up to several hundred kilometers. For example, cables with G.652 fiber can reach impressive lengths due to their low attenuation and dispersion properties. These cables can maintain signal integrity over vast distances, making them a staple in long-haul communication systems.
Here’s a quick look at typical single-mode distances:
- Standard single-mode fiber: Up to 100 kilometers without repeaters.
- Improved single-mode fiber: With special dispersion-compensating techniques, distances can extend to 200 kilometers or more.
Multimode Fiber Optic Cable Distances
On the other hand, multimode fiber is custom for short-distance applications. Its larger core allows multiple light paths, which is perfect for LAN backbones in office buildings or campuses. Multimode fiber is less expensive and easier to install, making it a go-to for local networks.
Typically, multimode fiber can stretch up to 2 kilometers. This makes it suitable for environments where high-speed connections are needed over shorter distances. It’s commonly used in:
- Office networks: Connecting computers and servers within a building.
- Campus networks: Linking multiple buildings in a single location.
The flexibility and cost-effectiveness of multimode fiber make it a popular choice for internal networks.

Both types of fiber optic cables have their unique advantages, depending on the application. Single-mode fiber excels in long-distance applications, while multimode fiber is ideal for short-distance, high-speed connections.
Next, we’ll explore the factors that can affect the range of fiber optic cables, such as attenuation and dispersion.
Factors Affecting Fiber Optic Cable Range
When discussing how far can fiber optic cable run, several key factors come into play. These factors determine how well the signal travels through the cable and how far it can go before needing a boost or amplification.
Attenuation
Attenuation refers to the loss of signal strength as light travels through the fiber optic cable. This is a natural occurrence and is influenced by the quality of the fiber and the distance the light has to travel. The lower the attenuation, the farther the signal can go without degrading.
- Single-mode fiber typically has lower attenuation compared to multimode fiber. This allows it to carry signals over longer distances, making it perfect for long-haul applications.
- Multimode fiber has higher attenuation, which limits its effective range to shorter distances, like those found in LANs.
To maximize range, choose cables with low attenuation ratings.
Dispersion
Dispersion is another critical factor. It occurs when different light waves travel at slightly different speeds through the fiber, causing the signal to spread out. Over long distances, this can lead to signal degradation.
- Single-mode fiber has minimal dispersion, which helps maintain signal clarity over extended distances.
- Multimode fiber experiences more dispersion due to its larger core, which allows multiple light paths. This is why it’s best suited for short distances.
Using dispersion-compensating techniques can help extend the range of fiber optic cables by reducing the effects of dispersion.
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
One of the advantages of fiber optic cables is their immunity to electromagnetic interference. Unlike copper cables, fiber optics do not conduct electricity, so they aren’t affected by EMI. This makes them ideal for environments with high levels of electrical noise.
- Fiber optic cables can be run alongside electrical cables without any risk of interference, ensuring a clean and reliable signal over long distances.
- Copper cables, on the other hand, can pick up EMI, leading to potential data loss and signal degradation.
By choosing fiber optics, you ensure a stable connection that’s free from the disruptions that can plague traditional metal cables.
Understanding these factors—attenuation, dispersion, and EMI—can help you make informed decisions about selecting and installing fiber optic cables for your specific needs. Next, we’ll compare fiber optic cables with their copper counterparts to see how they stack up in terms of signal loss and maximum distance.
Comparing Fiber Optic and Copper Cables
When it comes to selecting the best cabling for your network, understanding the differences between fiber optic and copper cables is crucial. Let’s explore how they compare in terms of signal loss, electromagnetic interference, and maximum distance.
Signal Loss
Signal loss, also known as attenuation, is a key concern in any cabling system. It refers to the reduction in signal strength as it travels through the cable.
- Fiber optic cables are known for their incredibly low signal loss. Light signals travel through glass fibers with minimal resistance, allowing them to maintain strength over long distances. For example, single-mode fiber can carry signals for several hundred kilometers before needing amplification.
- Copper cables, on the other hand, experience higher signal loss. Electrical signals weaken as they pass through the metal, limiting the effective range of copper cables to shorter distances. Typically, copper cables like Cat5e or Cat6 are limited to about 100 meters.
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
Electromagnetic interference can disrupt the transmission of data, causing errors and reducing the reliability of the network.
- Fiber optic cables are immune to EMI because they use light instead of electrical signals. This makes them ideal for environments with high electrical noise, such as industrial settings or areas with heavy machinery.
- Copper cables can pick up EMI from nearby electrical devices, potentially leading to data corruption or loss. Shielded variants of copper cables can reduce this risk, but they still can’t match the interference immunity of fiber optics.
Maximum Distance
The maximum distance a cable can effectively carry a signal is another important factor in network design.
- Fiber optic cables excel in long-distance applications. Single-mode fiber can transmit data over distances of up to 100 kilometers without a repeater, while multimode fiber is suitable for shorter distances, typically up to 2 kilometers.
- Copper cables are limited to much shorter distances. Standard Ethernet over copper is typically constrained to 100 meters, making it suitable for local area networks but not for long-haul communication.
In summary, when considering how far can fiber optic cable run, it’s clear that fiber optics outperform copper in terms of signal loss, EMI immunity, and maximum distance. This makes them the superior choice for high-performance, long-distance networks.
Next, we’ll address some frequently asked questions about fiber optic cable distances to further clarify their capabilities and applications.
Frequently Asked Questions about Fiber Optic Cable Distances
Is fiber optic good for long distances?
Absolutely! Fiber optic cables are excellent for long-distance data transmission. They carry information as light pulses through glass or plastic fibers, which results in very low signal loss. This means they can maintain a strong signal over much longer distances compared to traditional copper cables.
One of the standout features of fiber optics is their immunity to electromagnetic interference (EMI). This makes them ideal for environments with lots of electrical noise, like factories or areas with heavy equipment. Unlike copper cables, which can pick up interference from nearby electrical devices, fiber optics are not affected by EMI. This ensures a more reliable connection over long distances.
How far can fiber go without a repeater?
Single-mode fiber is the go-to choice for long-distance applications. It can transmit data over distances of up to 80-100 kilometers without the need for a repeater. This is thanks to its narrow core, which allows light to travel in a straight path, minimizing dispersion and attenuation.
For even longer distances, beyond 100 kilometers, repeaters or optical amplifiers can be used to boost the signal. This is common in submarine cables, where repeaters are placed every 50 to 100 kilometers to extend the reach even further.
What is the last mile of fiber optic cable?
The “last mile” refers to the final leg of the network that delivers internet and other services directly to homes or workplaces. It’s a critical part of network distribution because it connects the broader fiber optic infrastructure to individual users.
In many cases, the last mile can be one of the most challenging and costly parts of network deployment. This is because it often involves navigating urban environments or private properties. However, once installed, fiber optic cables provide fast, reliable internet access with minimal signal loss, even in the last mile.
Fiber optics are changing how we connect to the internet, making high-speed connections possible even in remote areas. This is why understanding how far can fiber optic cable run is crucial for planning and optimizing network infrastructure.
Next, we’ll explore how factors like attenuation and dispersion affect fiber optic cable range.
Conclusion
At AccuTech Communications, we understand the importance of a reliable and efficient network. That’s why we’ve been dedicated to providing top-notch fiber optic cabling solutions for over 30 years. Our expertise helps businesses across Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Rhode Island stay connected with minimal signal loss and maximum reliability.
Future-Proofing Your Network
Investing in fiber optic technology is a smart move for future-proofing your network. With the demand for higher bandwidth and faster speeds on the rise, fiber optics offer the scalability you need. Installing a fiber optic system today means you’re ready for tomorrow’s data demands without the need for costly upgrades.
Installation Tips for Optimal Performance
- Plan for Growth: When installing fiber optic cables, consider your current and future bandwidth needs. This foresight can save you from re-cabling in the future.
- Choose the Right Cable: Whether it’s single-mode for long distances or multimode for short-range applications, selecting the appropriate type is crucial for performance.
- Minimize Attenuation and Dispersion: Opt for cables with low attenuation and dispersion ratings to ensure your signal stays strong over long distances.
- Regular Maintenance: Keep your fiber optic network in peak condition with regular inspections and maintenance. This helps identify potential issues before they become major problems.
By partnering with AccuTech Communications, you can rest assured that your network infrastructure is in capable hands. Our commitment to quality and competitive pricing ensures you receive the best service possible. For more information on our fiber optic cabling services, visit our fiber optic cabling installation page.
Fiber optics are the backbone of modern communication, and with the right planning and installation, they can keep your business connected for years to come.