Types of Cables: Top 7 Amazing Choices in 2025
When it comes to ensuring a reliable electricity and power supply, understanding the types of cables is crucial. These cables are the backbone of any electrical and network system, providing the pathways for data and power transmission. Key types include electric cables for power transmission, network cables for data communication, and specialized cables designed for different environments and functions.
- Electric cables: Essential for household wiring and industrial power systems.
- Network cables: Facilitate data communication within and between devices.
- Armored cables: Provide added protection for outdoor and underground applications.
By choosing the right type for your needs, you can maximize safety and functionality. Cable safety features, such as insulation and shielding, protect users and equipment from hazards, ensuring efficient and secure operation across various settings.
My name is Corin Dolan. As the owner of AccuTech Communications, I’ve gained extensive expertise in the types of cables, offering businesses solutions custom to their network and power infrastructure needs.
Types of cables further reading:
– cabling installation
– structured cabling
– network installation services
Types of Cables
In today’s connected world, cables are everywhere. They power our homes, connect our devices, and keep our networks running smoothly. Let’s explore the types of cables that make all this possible.
Electric Cables
Electric cables are the workhorses of the electrical world. They carry power from one place to another, ensuring that homes, offices, and industries have the energy they need.
- Conductor: Usually made of copper or aluminum, conductors allow electricity to flow.
- Insulator: This is the protective layer that keeps the electricity safely inside the cable, preventing shocks and short circuits.
- Sheath: The outer covering that protects the insulator and conductor from environmental damage.
Electric cables come in various forms, such as non-metallic sheathed cables for residential wiring and armored cables for more demanding environments.
Network Cables
Network cables are the lifelines of our digital world. They connect computers, routers, and other devices, allowing them to communicate and share data.
- Twisted Pair Cables: These are common in home and office networks. They come in two types: Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) and Shielded Twisted Pair (STP).
- Coaxial Cables: Often used for video signals and TV connections, these cables have a single copper conductor at their core, surrounded by a layer of insulation and a metallic shield.
- Fiber Optic Cables: These are the high-speed champions of data transmission. They use light to send data quickly over long distances, making them ideal for telecommunications.
Power Cables
Power cables handle the big jobs. They transport electricity from power plants to homes and businesses, ensuring that everyone has the energy they need.
- Low Voltage Cables: Perfect for household wiring and small appliances. They are safe and easy to work with.
- Medium Voltage Cables: Used in larger buildings and industries, these cables can handle more power and are built to last.
- High Voltage Cables: These are the giants of the cable world, designed for long-distance transmission and high-power systems.
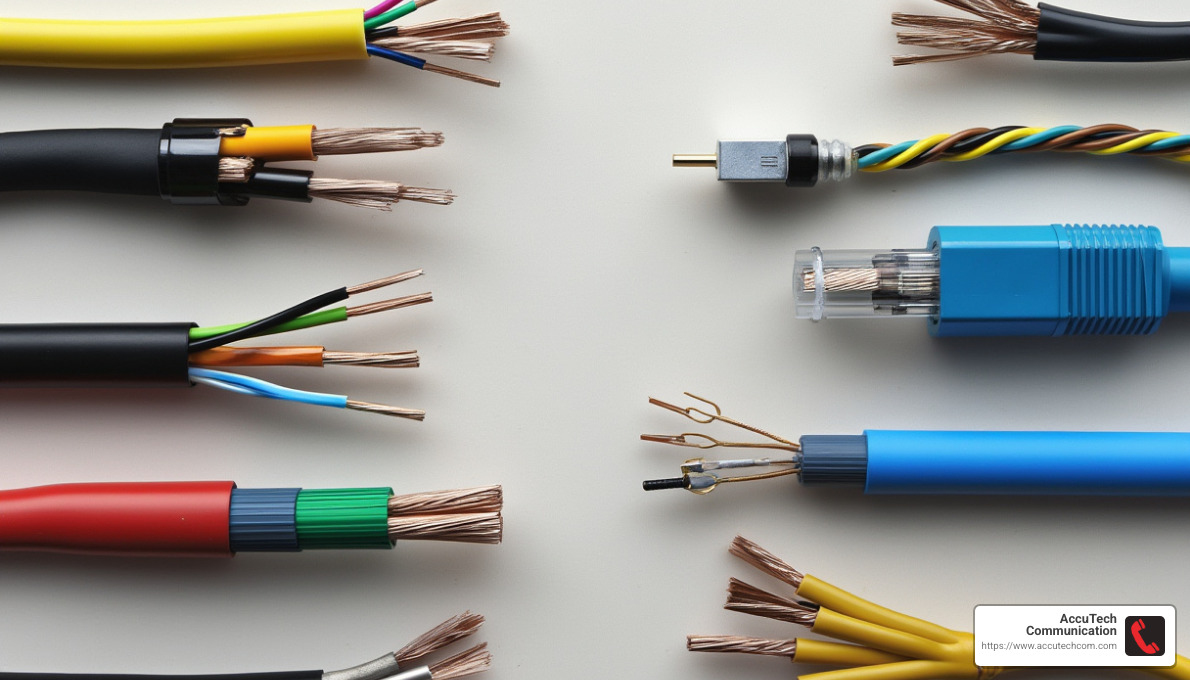
Choosing the right cable for your needs is essential. It ensures safety, reliability, and efficiency. Whether you’re setting up a home network or powering a factory, understanding the types of cables available will help you make the best choice.
Electrical Cables
Electric cables are crucial for delivering power safely and efficiently. Let’s explore two common types used in residential and more robust settings: Non-Metallic Sheathed Cable and Armored Cable.
Non-Metallic Sheathed Cable
Non-Metallic Sheathed Cable, often called NM cable, is a staple in residential wiring. These cables are made of multiple conductors, usually copper, which is known for its excellent conductivity. Each conductor is individually insulated to prevent electrical shocks and short circuits.
The insulator is wrapped in a non-metallic sheath, which provides an additional layer of protection. The sheath is typically made of plastic, making it flexible and easy to install in walls and ceilings. This flexibility is why NM cables are popular in homes. They are used for wiring outlets, switches, and other household electrical fixtures.
Armored Cable
For more demanding environments, Armored Cable (AC) or Metal Clad Cable (MC) is the go-to option. These cables are designed to withstand tougher conditions, offering more protection than NM cables.
Armored cables have a unique construction. They feature conductors insulated with a material like rubber or plastic, similar to NM cables. However, they add an extra layer: a metal sheath, often made of steel or aluminum. This metal sheath acts as a protective armor, safeguarding the cables from physical damage and interference.
- AC Cables: These have a metal sheath that can also serve as a grounding conductor. They are commonly used indoors where additional protection is needed.
- MC Cables: Similar to AC cables but with a separate grounding wire. They are versatile and can be used in both indoor and outdoor applications.
Armored cables are more expensive and rigid, making them less common in residential settings but ideal for industrial applications where durability is key. They ensure that power is delivered safely even in harsh conditions, providing peace of mind for critical systems.
Understanding these types of cables helps in choosing the right one for each application, ensuring safety and efficiency in electrical installations.
Network Cables
Network cables are the backbone of modern communication, enabling devices to connect and share data efficiently. Let’s explore three primary types of cables used in networking: Twisted Pair Cables, Coaxial Cables, and Fiber Optic Cables.
Twisted Pair Cables
Twisted pair cables are a staple in both telecommunication and networking. They consist of pairs of wires twisted together to reduce electromagnetic interference. This design is crucial for maintaining signal quality over distances.
- Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP): UTP cables are the most common type used in local area networks (LANs). They are affordable and easy to install, making them a favorite for home and office networks. Despite lacking additional shielding, they perform well in environments with minimal interference.
- Shielded Twisted Pair (STP): STP cables come with an extra layer of shielding around the twisted pairs. This makes them better suited for environments with higher interference, such as industrial settings. STP cables are slightly more expensive but offer improved protection against noise.
Coaxial Cables
Coaxial cables are designed to carry high-frequency signals with minimal loss. They feature a unique construction: a single copper conductor at the core, surrounded by a dielectric insulator, a metal shield, and an outer protective layer.
- Video Signals: Coaxial cables are widely used for transmitting video signals. They are commonly found in cable television setups, where they deliver clear and reliable TV connections.
- Internet Connectivity: In addition to TV, coaxial cables can also be used for internet connections. Their ability to handle high bandwidth makes them suitable for high-speed data transfer.
Fiber Optic Cables
Fiber optic cables represent the pinnacle of data transmission technology. They use thin strands of glass or plastic to transmit data as light signals, allowing for incredibly fast and reliable communication over long distances.
- Data Transmission: Fiber optic cables excel in high-speed data transmission, making them ideal for internet backbones and data centers. They can handle vast amounts of data without degradation over long distances.
- Telecommunications: In telecommunications, fiber optics enable high-quality voice and video calls. They offer unparalleled clarity and speed, essential for modern communication needs.

Choosing the right network cable depends on the specific requirements of your application. Whether it’s the cost-effective UTP for home networks, the robust STP for industrial environments, the reliable coaxial for TV and internet, or the lightning-fast fiber optic for high-speed data, each type plays a vital role in our connected world.
Power Cables
Power cables are essential for delivering electricity safely and efficiently across different environments. They come in various types, each designed to handle specific voltage levels and applications. Let’s explore three key categories: Low Voltage Cables, Medium Voltage Cables, and High Voltage Cables.
Low Voltage Cables
Low voltage cables are the workhorses of household wiring. They are designed to carry voltages up to 1,000 volts and are commonly used for small appliances and residential wiring.
- Household Wiring: In homes, low voltage cables are used for wiring light fixtures, outlets, and small appliances. They are typically insulated with materials like PVC to ensure safety and prevent electrical hazards.
- Small Appliances: These cables are also found in devices like lamps and kitchen appliances, where the power requirements are relatively low. Choosing the right cable ensures these appliances operate safely without overheating.
Medium Voltage Cables
Medium voltage cables are suited for larger buildings and industrial use, handling voltages between 1,000 and 35,000 volts. They are crucial for distributing electricity in commercial settings.
- Industrial Use: In factories and industrial complexes, medium voltage cables power heavy machinery and equipment. Their robust insulation, often made with materials like XLPE or HEPR, ensures they can withstand the demands of industrial environments.
- Larger Buildings: These cables are also used in larger commercial buildings where the electrical load is higher than in residential settings. Proper installation is key to maintaining safety and efficiency in these structures.
High Voltage Cables
High voltage cables are designed for long-distance transmission, handling voltages above 35,000 volts. They are vital for connecting power stations to the grid and delivering electricity over vast distances.
- Long-Distance Transmission: High voltage cables are the backbone of power systems, enabling electricity to travel from power plants to urban and rural areas. They are often used in overhead lines and underground systems.
- Power Systems: In power distribution networks, these cables ensure that electricity reaches consumers reliably. Their insulation must be of the highest quality to prevent energy loss and maintain system integrity.
Understanding the types of cables used in power distribution helps ensure that electricity is delivered safely and efficiently, whether it’s lighting up a home or powering an entire city. Each type of power cable has its unique role, custom to specific voltage levels and applications, ensuring that our modern world remains connected and powered.
Frequently Asked Questions about Types of Cables
When it comes to understanding the types of cables, there are some common questions that often arise. Let’s tackle these to clear up any confusion.
What are the 5 types of cable?
- Ribbon Cables: These are flat cables with many conducting wires running parallel to each other. They are often used in computers and printers because they can connect multiple points in a small space.
- Shielded Cables: These cables have an additional shield to protect against electromagnetic interference. They are useful in environments with a lot of electrical noise, ensuring clear signal transmission.
- Twisted Pair Cables: Widely used in networking, twisted pair cables consist of pairs of wires twisted together. This design helps reduce interference and is common in Ethernet networks.
- Coaxial Cables: These cables are used for transmitting video signals, like connecting televisions to antennas or cable boxes. Their design includes a central conductor, insulating layer, metallic shield, and an outer cover.
- Fiber Optic Cables: Known for high-speed data transmission, fiber optic cables use light to carry information. They are crucial in telecommunications and internet connectivity, offering high bandwidth and long-distance capabilities.
What are the 3 main cables?
- Twisted Pair: As mentioned, these cables are essential for network connections, particularly in local area networks (LANs).
- Coaxial: Used in both residential and commercial settings, coaxial cables are key for video transmission and broadband internet.
- Fiber Optic: These are the backbone of modern communication systems, enabling fast and reliable data transfer across vast distances.
What are the 7 types of cable network?
- Twisted Pair: Including both Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) and Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) varieties, these are fundamental for Ethernet connections.
- Coaxial: A staple in cable television and internet services, providing reliable video and data transmission.
- Fiber Optic: The go-to choice for high-speed internet and long-distance communication, offering superior performance.
- Crossover Cables: These are specialized twisted pair cables used to connect two devices of the same type directly, such as two computers.
- Cat5e-Cat7: These categories of twisted pair cables support different bandwidths and speeds, with Cat7 offering the highest performance for demanding networking environments.
- Patch Cables: Short cables used to connect devices to a network, often seen in data centers and office setups.
- Bulk Cables: Large quantities of cable used for extensive network installations, allowing custom lengths and configurations for specific needs.
Understanding these cable types helps ensure the right choice for each application, whether it’s setting up a home network or deploying a robust industrial communication system.
Conclusion
In today’s interconnected world, the right choice of cables is crucial to ensure seamless communication and reliable power supply. At AccuTech Communications, we understand the importance of having a well-structured cabling system, whether for data centers, business phone systems, or network installations.
Based in Massachusetts, our team has been a trusted partner in the region since 1993, offering certified and reliable services to businesses across Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Rhode Island. Our commitment to quality and competitive pricing makes us a preferred choice for many enterprises looking to optimize their network infrastructure.
Our expertise extends across various types of cables, from electrical and network cables to specialized solutions like fiber optics. This ensures that each client’s unique needs are met with precision and efficiency, whether it’s for high-speed data transmission or secure power distribution.
Choosing the right cables isn’t just about connectivity; it’s about building a foundation for your business’s success. With our comprehensive network cabling services, we help businesses create robust and reliable communication systems that support their growth and operational needs.
For businesses looking to improve their communication infrastructure, AccuTech Communications is here to provide expert guidance and top-notch service. Reach out to us today to learn more about how we can help you achieve your cable and network goals.

