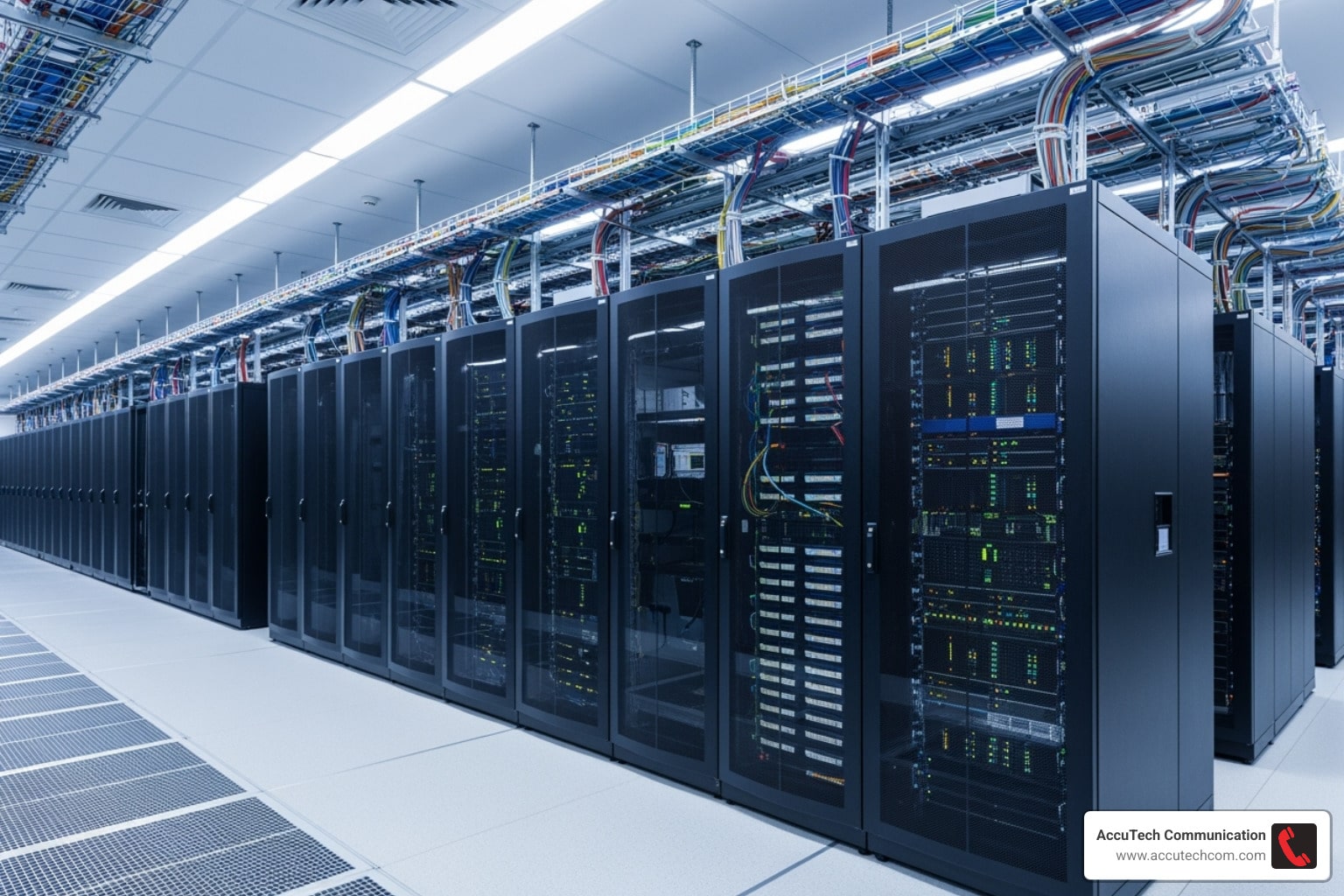
Data Center Cable Installation: 3 Steps to High Performance
Why Data Center Cable Installation Determines Your Network’s Future
Data center cable installation is the physical foundation that determines whether your network delivers reliable, high-speed performance or becomes a costly bottleneck. Here’s what you need to know:
Key Components of Data Center Cable Installation:
- Structured Cabling – Organized pathways following standards like TIA-942 for scalability and reliability
- Cable Types – Fiber optic (high-speed, long-distance), copper (cost-effective short runs), and power/grounding cables
- Proper Organization – Systematic labeling, airflow management, and adherence to bend radius requirements
- Testing & Standards – Validation using OLTS/OTDR equipment to ensure performance and future-proofing
Why It Matters: Poor cabling creates “spaghetti” tangles that block airflow, cause overheating, complicate troubleshooting, and risk equipment failure. A well-designed installation supports speeds from 10G to 400G+, reduces cooling costs by 10-20%, and adapts to technologies like AI and 5G.
Your data center is the heart of your business, and its performance depends on the physical network layer. Many organizations struggle with disorganized cabling that creates bottlenecks, drives up cooling costs, and makes maintenance a nightmare.
The difference between structured cabling and unstructured chaos is significant. A properly installed system allows IT teams to trace cables in minutes, ensures cooling systems work efficiently, and enables your network to scale from 10G to 400G without a complete overhaul.
Whether you’re building a new data center or upgrading an existing one, your installation methodology will impact operations for years. Standards like TIA-942 exist for a reason—they represent decades of lessons learned in demanding environments.
I’m Corin Dolan, and at AccuTech Communications, I’ve spent years helping businesses across Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Rhode Island design and install reliable data center cable infrastructure. We’ve seen how proper data center cable installation transforms operational efficiency and prepares businesses for future growth.

Basic data center cable installation terms:
Foundations of Data Center Cabling Infrastructure
Think of your data center’s cabling as its nervous system. If it doesn’t work properly, nothing else matters.
The Structured vs. Unstructured Divide
When it comes to data center cable installation, you have two paths: organized or chaotic. Unstructured, or “spaghetti,” cabling involves running cables directly from point A to B. This approach quickly leads to tangled messes, blocked airflow, and difficult troubleshooting.
Structured cabling follows established standards like TIA-942, using predefined pathways and a logical hierarchy. While it requires more upfront planning, the payoff is immense: easier maintenance, better airflow, simpler upgrades, and a system that makes sense. For reliable operations, structured cabling is essential. Learn more through our structured cabling services.
Key Components and Geography
Data centers rely on critical components working together. Patch panels act as central hubs for reconfiguring connections, network switches route data, and optical transceivers convert signals for high-speed fiber.
Modern data centers are organized into three functional zones:
- Main Distribution Area (MDA): The command center housing core routers and switches.
- Horizontal Distribution Area (HDA): The intermediary zone with switches and patch panels that branch out to racks.
- Equipment Distribution Area (EDA): Where servers, storage, and other network gear reside.
This modular design simplifies troubleshooting, upgrades, and capacity planning. The cabling strategy also depends on the data center type, whether it’s a private, public, or colocation facility, each with unique requirements.
Main Types of Data Center Cabling
Four main cable categories serve distinct purposes:
- Fiber optic cables: The speed demons of the data center, using light pulses for superior bandwidth and immunity to electromagnetic interference (EMI). They are ideal for moving massive amounts of data over long distances. Our fiber optic installation page has more details.
- Copper cables: Twisted pair cables (Cat6, Cat6a, etc.) are cost-effective workhorses for shorter runs. Their key advantage is Power over Ethernet (PoE), delivering data and power over a single cable.
- Power cables: These AC and DC lines distribute electricity to every component. DC power is often preferred in telecom for its efficiency.
- Grounding cables: This essential safety feature protects equipment from voltage surges and stabilizes power levels.
The Role of Key Hardware
Hardware ties the cabling infrastructure together:
- Media converters bridge different cable types, like copper to fiber, extending network reach.
- Network switches direct data traffic. Key selection criteria include port density, speed (10G, 40G, 100G+), and management features to prevent bottlenecks.
- Optical transceivers are hot-swappable modules that convert electrical signals to optical ones for fiber transmission. Matching them to speed and distance requirements is critical.
- Patch panels are the unsung heroes of maintainability. By terminating cables at a patch panel instead of directly to equipment, you create an organized interface for quick changes without disturbing critical systems.
Choosing Your Medium: Fiber Optic vs. Copper Cabling
One of the most critical decisions in data center cable installation is choosing between fiber optic and copper cabling. The best choice depends on your specific needs, including bandwidth requirements, distance, budget, and future-proofing.
Let’s break down both options.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Fiber Optic
Fiber optic cabling is the backbone of modern data centers, delivering top-tier performance.
Fiber’s superior speed and capacity are best, handling 100G, 400G, and beyond with minimal signal loss. This makes it ideal for AI workloads and real-time analytics. Its immunity to EMI means you can run it alongside power cables without signal degradation. Fiber is also highly scalable for 400G+ networks, making it a future-proof investment.
However, fiber has a higher initial cost for cables and components. It’s also more delicate, with bend radius sensitivity that requires careful handling during installation to prevent damage. Cleanliness is crucial, as contamination is a primary cause of failures.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Copper
Copper cabling remains an important and reliable part of modern data centers.
Its main advantage is cost-effectiveness for short distances, such as within a single rack. Another unique benefit is Power over Ethernet (PoE) capability, which allows a single cable to deliver both data and power to devices like IP cameras and wireless access points.
On the downside, copper’s larger cable diameter can block airflow and reduce cooling efficiency. It’s also susceptible to crosstalk and EMI, which can degrade signal quality. Finally, copper has speed and distance limitations, struggling with the high-speed, long-distance demands of modern applications.
Comparing Fiber Optic and Copper Cabling
| Feature | Fiber Optic Cabling | Copper Cabling |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Very High (100G, 400G, 800G+) | Moderate (1G, 10G, 40G for short distances) |
| Distance | Very Long (kilometers) | Short (up to 100 meters for Ethernet) |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower initial investment |
| Durability | More delicate, sensitive to bend radius | More robust, less sensitive to bend radius |
| Security | Very High (no EMI, difficult to tap) | Moderate (susceptible to EMI, easier to tap) |
| Airflow Impact | Low (smaller diameter) | High (larger diameter, can block airflow) |
| PoE | No (requires separate power) | Yes (can deliver power and data) |
| EMI | Immune | Susceptible to interference |
Most data centers use a hybrid approach: fiber for high-speed backbone connections and copper for shorter runs and PoE devices. Understanding the strengths of each helps you design a balanced and effective data center cable installation.
Mastering Data Center Cable Installation: A Step-by-Step Guide
A successful data center cable installation is a lifecycle that starts with careful planning and extends through maintenance and upgrades. Cutting corners in any phase leads to future problems.
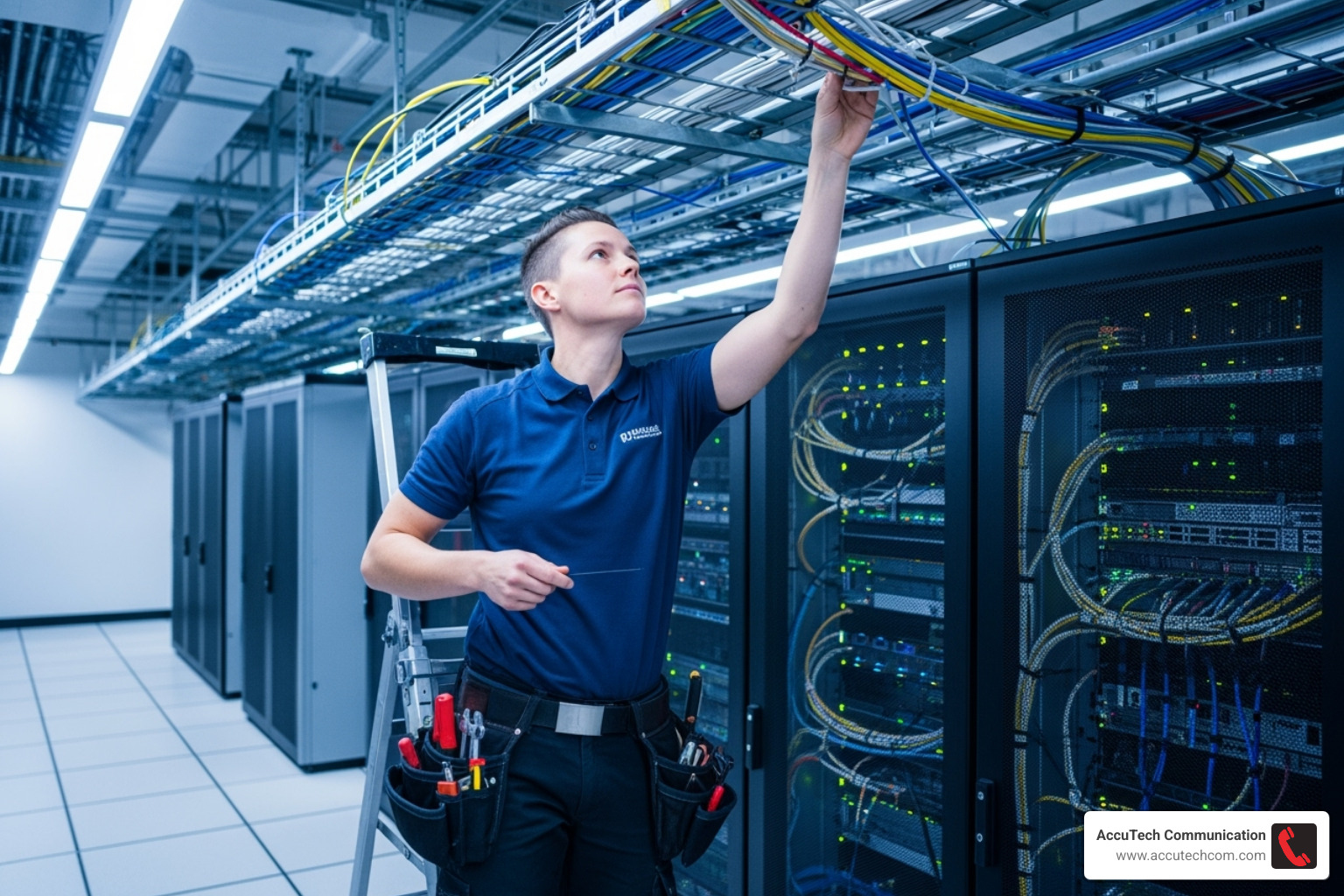

Step 1: Planning, Design, and Documentation
This phase is where projects succeed or fail. Rushing it guarantees future headaches.
- Visual Design: Create detailed maps of every connection and the physical layout of racks and pathways. This ensures cables run efficiently.
- Scalability Planning: Design for future growth. With bandwidth demands growing 50-75% annually, use modular components and oversized pathways to make expansion straightforward.
- Detailed Documentation: Record every cable type, length, termination point, and pathway. Standardized naming conventions and digital records are invaluable for troubleshooting and upgrades.
- Change Management: Implement clear procedures for tracking and approving modifications to prevent undocumented changes from creating chaos.
- Industry Standards: Adhere to standards like TIA-942, ISO/IEC 11801, and ANSI/BICSI 002. They provide proven guidelines for reliability and performance.
Step 2: Managing Pathways and Airflow
Cable management and cooling efficiency are inseparable. Poor routing costs real money in increased energy consumption.
- Pathways: While traditional data centers used raised floors, this can block airflow. The preferred modern approach is overhead wiring using cable trays. Careful routing with one-way flows prevents crossovers and blockages.
- Cable Tray Fill Ratios: Follow NEC and TIA guidelines, which recommend not exceeding a 40-50% fill ratio. This ensures proper airflow and prevents cable overheating.
- Cooling Impact: Proper cable management can reduce cooling costs by 10-20%. It allows systems like hot aisle/cold aisle containment to work effectively, improving your Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE).
Step 3: Organization, Labeling, and Safety
An organized system transforms daily operations, making troubleshooting and upgrades simple.
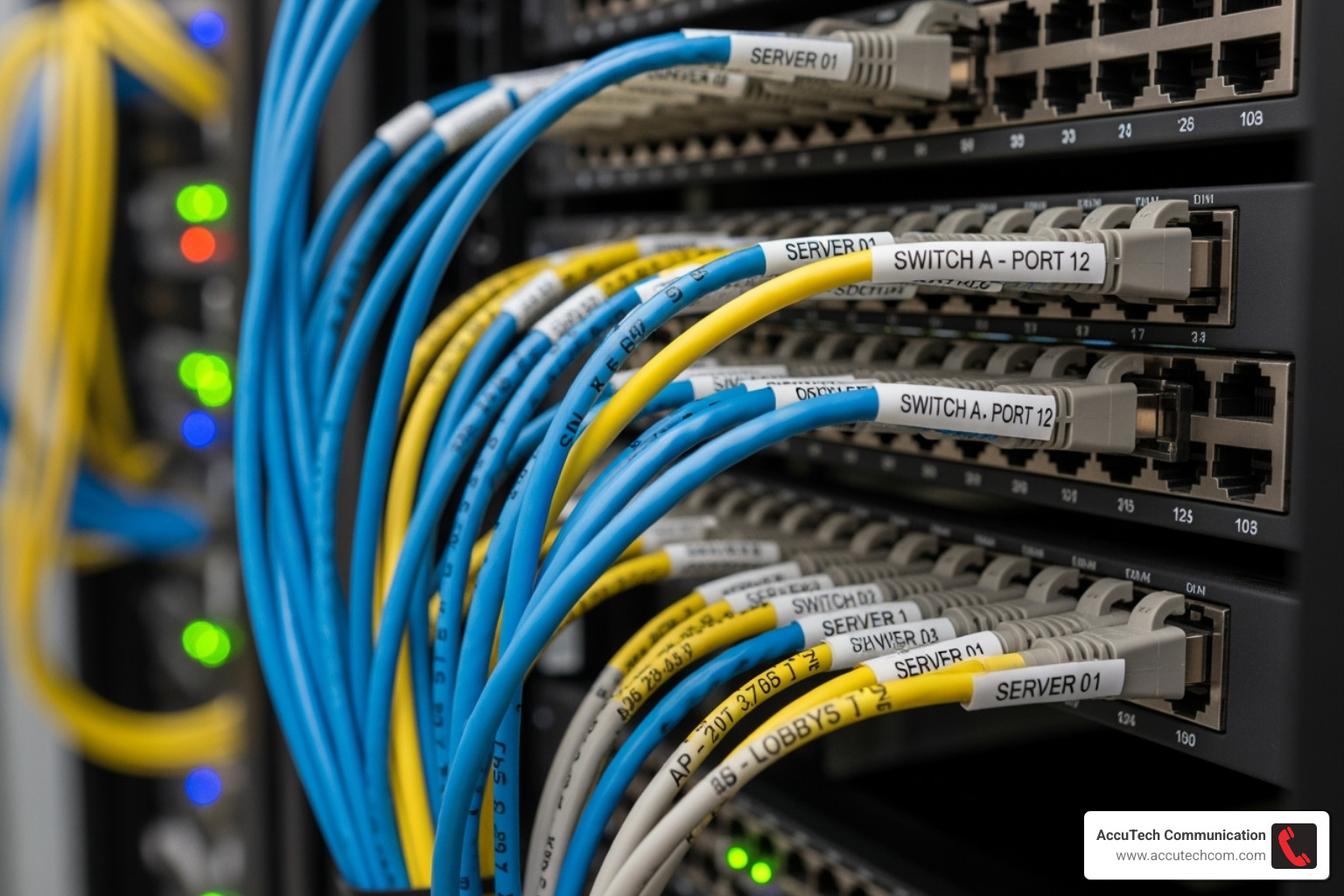

- Systematic Labeling: Use a clear, consistent system that labels both ends of every cable, tracing it from origin to destination. This can cut troubleshooting time in half.
- Fire Safety: Ensure fire suppression systems have unobstructed access. Using plenum-rated cables in air-handling spaces is a requirement for compliance.
- Abandoned Cables: These are not harmless. They obstruct airflow, complicate maintenance, and pose a fire hazard. Proper decommissioning involves removing, not just disconnecting, unused cables.
- Bend Radius: Use horizontal and vertical cable managers to prevent sharp bends that can damage cables, especially sensitive fiber optics, and cause signal loss.
For comprehensive support, explore our network cabling installation services. We ensure your data center cable installation sets you up for long-term success.
Standards, Testing, and Future-Proofing Your Network
Your data center’s cabling is a living system that must adapt. Following standards, testing protocols, and planning for future capacity will determine whether your network thrives. A standards-based design avoids costly reworks and maximizes uptime.
For more information on ensuring your network cabling is up to par, explore our network cabling installation services.
The Role of Industry Standards and Testing
Industry standards are the shared language ensuring all components work together. Organizations like the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA), BICSI, and ISO/IEC provide guidelines refined over decades.
TIA-942 is crucial for data center cable installation, specifying design and implementation for telecommunications infrastructure. Compliance ensures your cabling meets performance requirements, supports future applications, and provides a safe environment.
However, standards are only useful if you verify compliance through cable testing and validation. Every cable must be tested for connectivity and signal integrity.
- Fiber Optic Testing: Tier 1 certification uses an Optical Loss Test Set (OLTS) to measure total signal loss. Tier 2 certification uses an Optical Time Domain Reflectometer (OTDR) to pinpoint where losses occur.
- MPO & Contamination: For high-bandwidth MPO connectors, proper polarity is critical for function. Contamination is the #1 cause of fiber-related test failures, so keeping end faces clean is essential.
Future-Proofing for Evolving Technologies
The technology landscape shifts constantly. Your infrastructure must accommodate tomorrow’s demands from AI, machine learning, and 5G, which are already generating exponential data growth.
Edge computing also reshapes design, requiring scalable cabling in smaller, distributed environments. Speeds are also climbing, with 25G and 50G becoming common, and 100G, 400G, and even 800G on the horizon. Selecting the right cabling, like OM5 multi-mode or single-mode fiber, supports these future speeds without a complete overhaul.
Key considerations for a scalable infrastructure include using modular components, budgeting for 20-30% excess capacity, using oversized conduits, and tracking network metrics to anticipate needs. The goal is to build flexibility into your infrastructure so you can adapt as new technologies emerge.
Frequently Asked Questions about Data Center Cabling
We’ve helped dozens of businesses across Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Rhode Island with data center cable installation. Here are answers to some common questions.
What is the difference between structured and unstructured cabling?
Structured cabling is a standardized, organized approach using predefined pathways, patch panels, and cable trays. It’s designed for scalability and reliability, making upgrades and troubleshooting simple.
Unstructured cabling is a point-to-point method without a systematic plan. It quickly devolves into “spaghetti cabling” that blocks airflow, complicates maintenance, and increases the risk of downtime. For modern data centers, structured cabling is essential.
Why is removing abandoned cables so important?
Abandoned cables are not harmless. They obstruct airflow, which increases cooling costs and can cause equipment to overheat. They also create clutter that complicates maintenance and poses a significant fire hazard, potentially violating electrical codes and affecting insurance coverage. Proper decommissioning improves safety, efficiency, and manageability.
How does cabling choice impact data center cooling?
Cabling has a direct impact on your cooling bills. Dense, bulky cables can block airflow, creating hot spots and forcing your HVAC system to work harder. Proper cable management—using overhead trays, respecting fill ratios, and choosing smaller diameter cables like fiber optics—improves airflow dramatically. This reduces cooling requirements and lowers your Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE), saving money and energy.
Your Blueprint for a High-Performance Network
We’ve covered the essentials: from structured cabling principles and choosing between fiber and copper to the step-by-step process of installation and maintenance. The key takeaway is that your data center’s physical layer is the foundation that either enables or constrains your business.
A proper data center cable installation means your IT team works efficiently, your cooling systems are effective, and your network can scale to meet future demands. When it’s done poorly, you face tangled cables, rising costs, and the constant risk of downtime.
The good news is you don’t have to figure this out alone. Professional installation is about leveraging experience to anticipate problems, design for your specific needs, and get it right the first time.
At AccuTech Communications, we’ve been building reliable network foundations for businesses across Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Rhode Island since 1993. We’ve helped clients in healthcare, manufacturing, and other industries scale their infrastructure as technology has evolved from 100 Megabit to 400 Gigabit speeds. Our certified team brings practical experience from hundreds of successful installations.
Your data center deserves a professionally installed cabling infrastructure that delivers reliable performance today and adapts for tomorrow. Whether you’re building, upgrading, or untangling an existing facility, we’re here to help.
Contact us for your data center cable installation needs and let’s discuss a practical plan for your business and budget. We offer straightforward advice from people who care about getting it right.

