How is Fiber Optic Cable Made: Top 3 Secrets Revealed
How is fiber optic cable made? Changing raw glass into a medium for transmitting light is a fascinating process, critical to modern communications. Highlighted by the sophistication of light pulses traveling at breathtaking speeds, fiber optic technology has revolutionized data transmission by replacing traditional copper wires with thin strands of glass. These strands, as thin as a human hair, efficiently carry vast amounts of data across great distances. Here’s a quick look at how this is achieved:
- Core: Ultra-pure silica glass where light travels.
- Cladding: Ensures light stays within the core.
- Coating: Protects and organizes fibers.
Fiber optic cables support high-speed data transfer, essential for industries like healthcare, where robust communication systems are non-negotiable.
As the owner of AccuTech Communications, I’ve managed and optimized countless network solutions, ensuring our clients experience seamless data flow. My background equips me with an in-depth understanding related to how is fiber optic cable made, and I’m here to guide you through the nuances of this vital technology.
How is fiber optic cable made word roundup:
What are Fiber Optic Cables Made Of?
Fiber optic cables are the backbone of modern communication, made from materials that maximize data transmission efficiency. At their core, these cables rely on silica glass and polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) to function.
Core
The heart of a fiber optic cable is the core, typically made of ultra-pure silica glass. This is where light signals travel, carrying data over vast distances. Silica glass is favored for its excellent light transmission properties, making it ideal for long-distance telecommunications.
Cladding
Surrounding the core is the cladding, another layer of glass with a slightly lower refractive index. This difference in refractive index is crucial as it keeps the light signals contained within the core through a phenomenon called total internal reflection. This means the light bounces within the core, allowing it to travel long distances with minimal loss.
Coating
The coating is the protective layer wrapped around the cladding. It’s typically made from plastic materials like polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA). The coating serves multiple purposes:
- Protection: Shields the delicate glass core and cladding from physical damage.
- Flexibility: Allows the fibers to bend without breaking.
- Identification: Different coatings can help identify specific fibers within a cable bundle.
Polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA)
In some fiber optic cables, particularly those used for short-distance or specialty applications, the core or cladding might be made from polymethylmethacrylate. PMMA is a type of plastic known for its clarity and durability. Although it doesn’t offer the same performance as silica glass, it is used in environments where flexibility and cost are more critical than long-distance data transmission.
Fiber optic cables, with their intricate construction of core, cladding, and coating, are marvels of modern engineering. By using materials like silica glass and PMMA, these cables provide high-speed data transfer capabilities that are essential in today’s interconnected world.
Next, let’s dig into the fascinating process of how is fiber optic cable made, exploring the steps from raw materials to finished product.
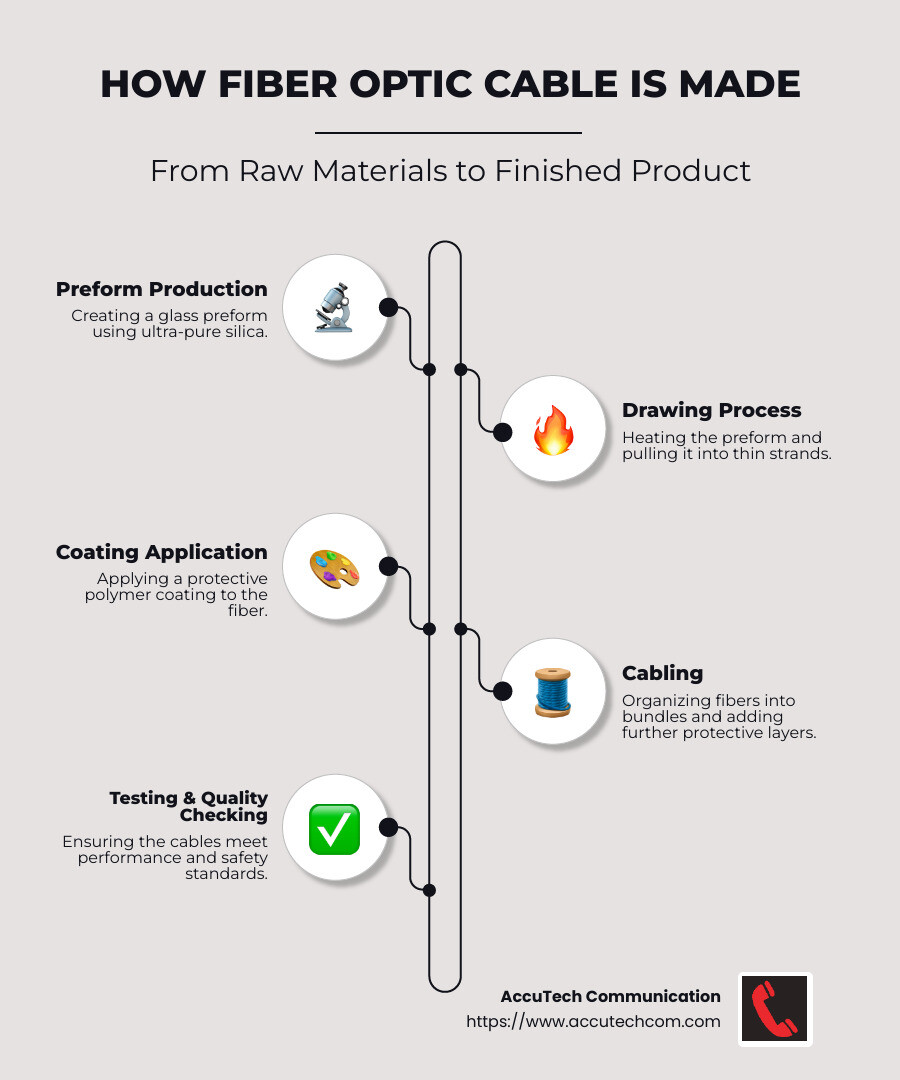
How is Fiber Optic Cable Made?
Creating fiber optic cables is a meticulous process that transforms raw materials into powerful communication tools. Let’s break down the key steps: preform production, drawing process, coating application, and cabling.
Preform Production
The journey of a fiber optic cable starts with the creation of a glass preform. This is a large, cylindrical piece of ultra-pure silica glass. The preform is crafted through methods like Modified Chemical Vapor Deposition (MCVD), where chloride gases are injected into a rotating silica tube. As these gases heat up to around 1500 degrees Celsius, they deposit layers inside the tube, forming the core and cladding structure.
Drawing Process
Once the preform is ready, it moves to the drawing tower. Here, the preform is heated to approximately 2000 degrees Celsius until it becomes malleable. The softened glass is then drawn into a thin strand, forming the core and cladding of the fiber. This strand, measured in microns, can stretch up to 5 kilometers from a single preform. A diameter gauge ensures the fiber maintains a consistent size throughout this process.
Coating Application
After drawing, the fiber needs protection. This is where the coating application comes in. The fiber is passed through a machine that applies a thin layer of protective coating, often made from plastic materials. The coating doesn’t contribute much to the strength but prevents scratches and makes handling easier. This step is crucial for the fiber’s longevity and functionality.
Cabling
Even though individual fibers can carry a significant amount of data, they are typically bundled into cables for added protection and easier installation. These bundles might contain 12, 24, or even more strands, housed within a protective jacket. The fibers are organized into ribbons or tubes, depending on the cable type. This arrangement ensures durability and ease of deployment, whether the cables are laid underground or underwater.
Fiber optic cables are a testament to modern engineering, crafted through a series of precise steps. Each phase, from preform production to cabling, is essential in creating cables that power our digital world with speed and reliability.
The 3 Cs of Fiber Optics
Fiber optic cables are crafted with precision, and their effectiveness hinges on three critical components: core, cladding, and coating. Let’s explore these elements to understand their roles in making fiber optics a powerful communication tool.
Core
The core is the heart of the fiber optic cable. It’s where the magic happens—where light signals carrying data travel. Made from ultra-pure silica glass, the core’s purity is crucial. This purity ensures that the light can travel long distances without degrading, maintaining the integrity of the data transmitted. Imagine a crystal-clear highway for light, free from obstacles and interference. That’s the core’s job in a nutshell.
Cladding
Surrounding the core is the cladding, another layer of glass with a slightly different refractive index. The cladding acts like a mirror, reflecting light back into the core. This reflection is essential because it keeps the light bouncing within the core, following a zig-zag path through a process called total internal reflection. Without the cladding, light would escape, and data transmission would fail. It’s like having guardrails on that crystal-clear highway, ensuring the light stays on course.
Coating
Finally, the coating provides the fiber with protection from the outside world. While the core and cladding are all about maintaining light integrity, the coating focuses on durability. Typically made from plastic or other resilient materials, the coating shields the fiber from physical damage, like scratches or environmental wear. It also aids in handling and organizing the fibers during installation. Think of the coating as a robust outer shell, safeguarding the delicate components inside.

Each of these components plays a vital role in the fiber optic cable’s performance. Together, they create a system that can transmit vast amounts of data at lightning speed, revolutionizing how we communicate and connect.
Next, we’ll dig into the manufacturing process of fiber optic cables, exploring how these components come together to form the backbone of our digital world.
Manufacturing Process of Fiber Optic Cables
Creating a fiber optic cable is like crafting a masterpiece. It involves several intricate steps to ensure the cable performs at its best. Let’s explore the process from start to finish.
Laydown & Consolidation
The journey begins with laydown, where raw materials are transformed into glass. Silica, combined with chemicals like silicon tetrachloride and germanium tetrachloride, is crystallized into a fluffy, white form. This process is akin to spinning cotton candy, where the glass collects on a rotating stick in an oven.
Once the glass has formed, it undergoes consolidation. In this stage, the fluffy glass pillars are heated in a furnace at over 1,000 degrees Fahrenheit. This “cooking” process purifies the glass, removing impurities that could disrupt data transmission. The result? Clear glass pillars, ready for the next step.
Draw
Next, these glass pillars are transformed into thin strands in the draw process. The pillars are placed in a vertical furnace, where they melt and drip down, forming a fine glass thread. This thread is pulled through a machine that ensures it maintains a uniform thickness. Each pillar can produce miles of fiber, changing it from a chunky glass pillar into a slender, light-conducting strand.
Coating
After the draw, the delicate glass fibers receive a protective coating. This layer doesn’t just protect the fiber from scratches and environmental damage; it also makes the fibers easier to handle. The coating is applied as the fiber is spooled onto reels, ensuring each strand is ready for installation.
Cabling
Finally, the individual fibers are bundled into cables. This step involves organizing fibers into ribbons or tubes, which are then housed within a protective jacket. The type of cabling—whether stranded or central tube—depends on the intended application. Stranded cables are flexible and allow for frequent access, while central tube cables offer higher fiber density.
Throughout these stages, precision is key. Each element, from the glass core to the outer jacket, plays a specific role in ensuring the fiber optic cable can deliver high-speed, reliable data transmission.
In the next section, we’ll answer some frequently asked questions about fiber optic cables, diving deeper into the materials and construction techniques that make these cables so effective.
Frequently Asked Questions about Fiber Optic Cables
What are the raw materials for fiber optic cable?
Fiber optic cables start with a few essential materials. Quartz is the primary ingredient, known for its purity and optical clarity. It’s combined with pure oxygen and germanium to create the perfect glass mixture. This combination ensures that the fiber can transmit light over long distances without losing signal quality.
How do you make a fiber optic cable?
Fiber optic cable manufacturing involves several key steps:
- Preform Production: The process begins with creating a glass preform, a large cylinder of ultra-pure glass. This preform is made by depositing layers of silica and other chemicals inside a silica tube. This step is crucial as it defines the fiber’s future properties.
- Drawing Process: The preform is heated in a draw tower, where it melts and stretches into a thin strand of fiber. This stage is like pulling taffy, ensuring the fiber has a consistent diameter.
- Coating Application: Once drawn, the fiber receives a protective coating. This layer shields the fiber from physical damage and environmental factors, ensuring durability.
- Cabling: Finally, the fibers are bundled into cables. They are organized into structures like ribbons or tubes before being encased in a protective jacket. This step determines whether the cable will be a stranded or central tube type, depending on its intended use.
How is optical fiber constructed?
Optical fiber construction involves three main components:
- Core: This is the central part of the fiber, made from ultra-pure glass. It’s responsible for carrying light signals.
- Cladding: Surrounding the core, the cladding has a different refractive index. It reflects light back into the core, allowing the signal to travel long distances with minimal loss.
- Protective Layer: The outermost layer is a protective coating that guards against physical damage and environmental exposure, ensuring the fiber remains intact and functional.
These components work together to enable high-speed data transmission, making fiber optic cables an essential part of modern connectivity.
In the next section, we’ll explore the 3 Cs of fiber optics: core, cladding, and coating, to understand their individual roles in the performance of these cables.
Conclusion
At AccuTech Communications, we pride ourselves on being at the forefront of fiber optic technology, delivering reliable network cabling solutions across Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Rhode Island since 1993. Our commitment to quality and certified service ensures that businesses in these regions can rely on us for their connectivity needs.
Fiber optic cables have revolutionized the way we communicate, offering unparalleled speed and reliability. The longevity of these cables is one of their standout features. Made from ultra-pure materials like quartz and protected by robust coatings, fiber optic cables are designed to withstand the test of time. This durability means fewer replacements and lower maintenance costs over the years, making them a cost-effective solution for businesses looking to future-proof their network infrastructure.

As we look to the future, the role of fiber optic cables in connectivity will only expand. With the rise of smart cities, the Internet of Things (IoT), and advances in AI computing centers, the demand for high-speed, reliable data transmission is greater than ever. Fiber optics will be at the heart of this change, enabling innovations that were once thought impossible.
Whether it’s powering next-generation AI applications or supporting the infrastructure of smart cities, fiber optic technology is set to play a crucial role. At AccuTech Communications, we’re excited to be part of this journey, helping businesses harness the power of fiber optics for a brighter, more connected future.
For more information on how we can help you with fiber optic cabling installation, visit our Fiber Optic Cabling Installation page.

