Ensuring Network Health: Your Guide to the RJ45 Cable Tester
Knowing how to use rj45 network cable tester is essential for maintaining a healthy network. These tools quickly find cable problems, reducing downtime and ensuring your system runs smoothly. A reliable network is the backbone of any business, and a cable tester helps you pinpoint issues like broken wires or incorrect setups before they cause major slowdowns.
Here’s a quick guide:
- Connect the cable: Plug each end of the RJ45 cable into the tester’s main and remote units.
- Power on: Turn the tester on.
- Run the test: Press the “Test” button.
- Watch the lights: Observe the sequence of LED lights on both units.
- Interpret results: If all lights flash in order on both ends, the cable is good. Missing or out-of-order lights indicate a fault.
With over 30 years of experience, I, Corin Dolan, owner of AccuTech Communications, have used my expertise in how to use rj45 network cable tester to help businesses across Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Rhode Island build reliable network infrastructures. We ensure your communication backbone is robust and ready for anything.
Simple guide to how to use rj45 network cable tester:
What is an RJ45 Network Cable Tester and Why is it Crucial?
When your internet slows down or file transfers fail, a faulty cable is often the culprit. An RJ45 network cable tester is an essential tool that diagnoses the physical health of your network cables, helping you find out exactly what went wrong and where. Learning how to use rj45 network cable tester is a key skill for any business owner or tech-savvy individual.
Most testers have two parts: a main unit and a remote unit. You plug each end of a cable into a unit, and the tester sends signals through each wire to verify the connection. This process is crucial because faulty cables cause slow speeds, dropped connections, and costly downtime. By testing cables, you prevent these issues and ensure data travels quickly and cleanly. For more on network building blocks, see our guides on Network Cables and Ethernet Cable Types.
The Three Tiers of Cable Testing
Cable testing has different levels of complexity, each suited for different needs.
- Validation Testing: This is the most basic test and the foundation of learning how to use rj45 network cable tester. It checks for physical integrity: Are there broken wires (opens), wires touching (shorts), or wires in the wrong order (wiremap)? This is your essential, go-to check.
- Qualification Testing: This level goes beyond basic connectivity to ask, “can it perform?” Qualification testers check if a cable can support high speeds like 1 or 10 Gigabit Ethernet by sending actual data through it. This is ideal for troubleshooting mysterious slowdowns or verifying if older cabling can handle new equipment.
- Certification Testing: This is the highest level of testing, using specialized equipment to prove a cabling system meets strict industry standards from bodies like TIA or ISO/IEC. It provides a definitive “pass” or “fail” report, often required for professional and commercial installations. It’s the gold standard for guaranteeing network performance and compliance. Learn more about The Importance of Professional Cabling Installation for Your Business.
Common Problems a Tester Can Find
A network cable tester is a master at uncovering common issues that disrupt your network:
- Open Circuit: A wire is broken or disconnected, creating a dead end for data.
- Short Circuit: Two or more wires are touching, scrambling data signals.
- Miswires: Wires are connected but in the wrong order. A crossover cable is an intentional miswire used to connect two similar devices directly.
- Improper Termination: The RJ45 connector wasn’t installed correctly, leading to poor contact.
- Physical Cable Damage: A crushed or sharply bent cable can have internal damage that a tester can find.
- Wrong Wiring Standard: Using T568A on one end and T568B on the other (unless creating a crossover cable) will be flagged as a miswire.
Understanding these common faults is why mastering how to use rj45 network cable tester is so valuable. To avoid these issues, see our guide on 5 Common Mistakes to Avoid When Installing Network Cabling.
Pre-Test Checklist: What to Do Before You Begin
A few preparatory steps ensure accurate results and save you headaches later. Think of this as a pre-flight check for your cable testing.
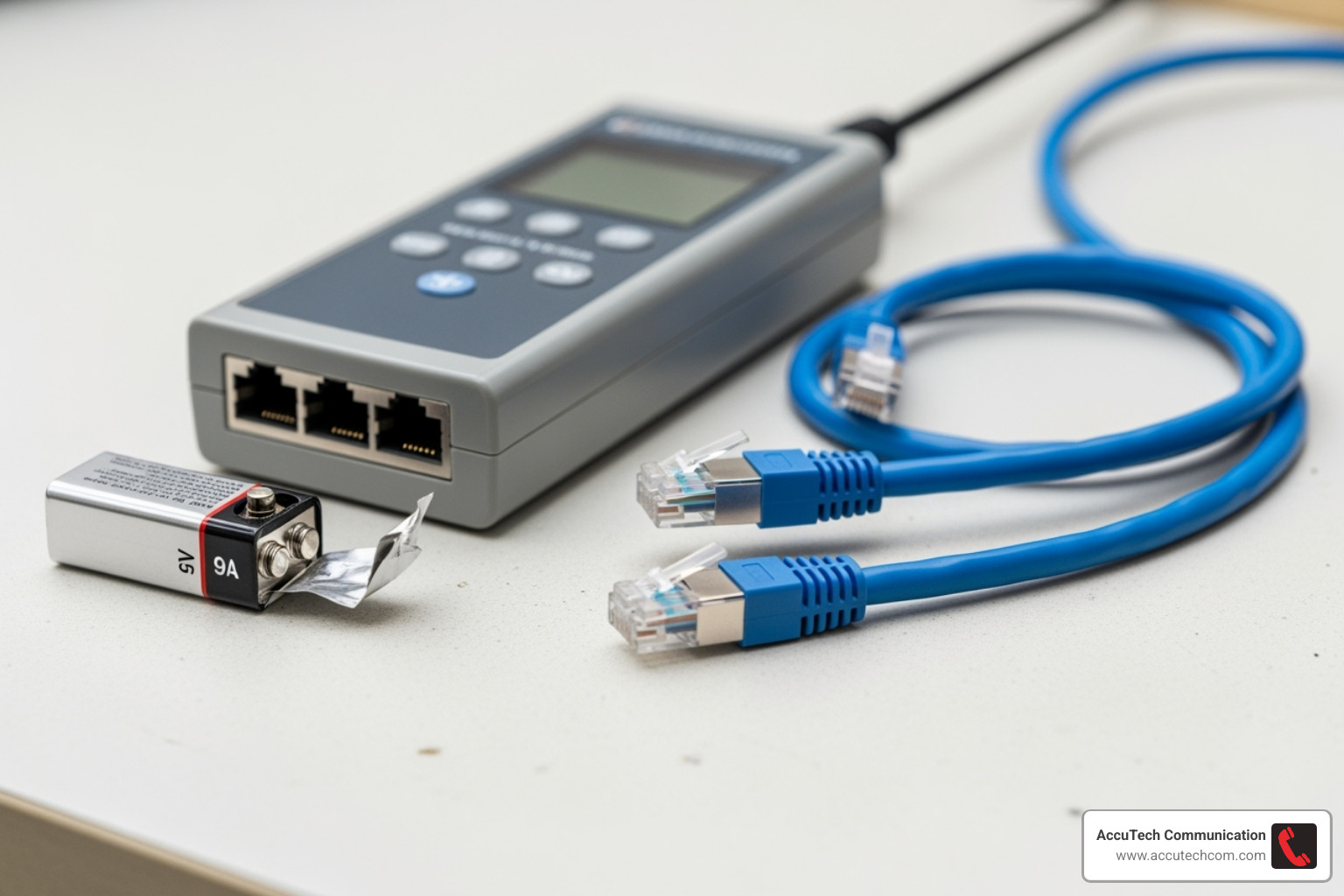

- Check Your Equipment: Give your tester a quick visual inspection for any damage. Ensure it’s clean and in good working order.
- Check the Battery: Most testers are battery-powered. Check for a low-battery indicator or test the batteries before you start. Power on the tester to confirm it’s ready.
- Test the Tester: A golden rule for how to use rj45 network cable tester is to first test your tester. Use a known-good patch cable to run a quick test. This confirms the tester is working and shows you what a perfect result looks like.
- Inspect the Cable: Visually inspect the cable you’re about to test for kinks, cuts, or severe bends. Pay close attention to the RJ45 connectors for any bent or broken pins.
- Ensure a Secure Connection: When you plug the cable into the tester, make sure the RJ45 connector is fully inserted and clicks securely into place. A loose connection will cause a false reading.
How to Use an RJ45 Network Cable Tester: A Step-by-Step Guide
Now that you’re prepped, let’s walk through the simple process of testing a cable. These devices are user-friendly, making them accessible to everyone. For more on wiring fundamentals, check our resources on Network Cable Wiring and Cat6 cabling.
Step 1: Connecting the Cable for Testing
Proper connection is key for accurate results. Your approach will vary slightly depending on what you’re testing.
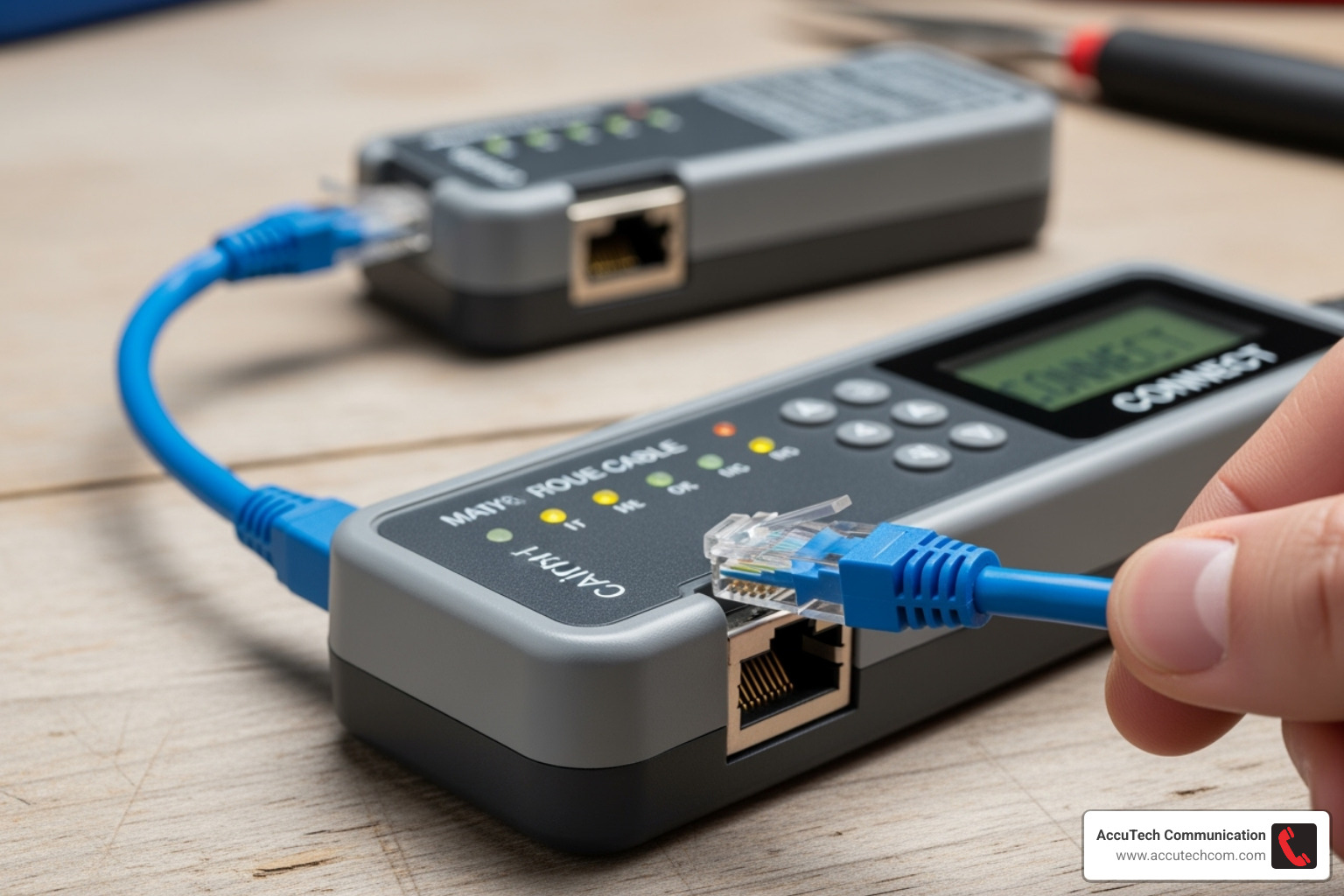

- Patch Cables: For shorter cables, plug one end into the tester’s main unit (TX) and the other into the remote unit (RX). Ensure both connectors click securely into place.
- In-Wall Cable Runs: For installed cabling, connect one end (e.g., at a wall outlet) to the main unit. Take the remote unit to the other end of the cable (e.g., in a server closet) and plug it in there.
- Wall Jacks: To test a wall jack, use a known-good patch cord. Plug one end into the jack and the other into your tester.
Step 2: Operating the Tester
With the cable connected, it’s time to start the test.
Press the power button to turn the device on. Then, select the appropriate test function, which is usually a single “Test” button for standard continuity checks. Most modern testers run in an automatic mode, cycling through the wire pairs for you. Some may have a manual mode or a ‘S’ (Slow) mode, which slows down the test cycle to make the lights easier to observe.
Step 3: Running the Test and Observing the Lights
Press the ‘Test’ button to begin. The tester will send a current through each wire in the cable.
Watch the sequential LED lights on both the main and remote units. These lights are typically numbered 1-8, with an additional ‘G’ light for the ground connection on shielded cables. For a healthy cable, the lights will illuminate in the exact same sequence (e.g., 1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8) on both units simultaneously. This synchronized pattern confirms your cable is wired correctly.
To see this in action, we recommend you Watch a basic cable test in action. This helps visualize the LED patterns of a successful test.
Decoding the Results: How to Interpret LED Light Patterns
Now it’s time to read the language of the blinking lights. Understanding these patterns is the key to quick fault diagnosis. A basic tester performs a pin-to-pin test, checking the connection for each wire. Mastering how to use rj45 network cable tester means learning what these common light patterns signify.

Good Cable (Straight-Through)
This is the ideal result. You will see all lights 1-8 illuminate in sequence on both the main and remote units. The sequence will be identical and synchronized, confirming each wire is correctly connected. If you are testing a shielded cable, the ‘G’ light for ground should also light up. This indicates your cable is ready to support reliable data flow for applications like Network Cable for Gigabit Ethernet.
Open Circuit
An open circuit means a wire is broken or disconnected. You’ll know you have an open when one or more corresponding lights do not light up on either the main or remote unit. For example, if pin 3 is open, the #3 light will remain dark on both ends. This signals a physical break or a bad termination.
Short Circuit
A short occurs when two or more wires touch. The tester will typically show two or more lights illuminating simultaneously on the main tester, while the remote tester shows no lights or inconsistent lights for those pins. This is a serious fault that can disrupt signals and must be fixed.
Miswire or Crossover Cable
A miswire means the wires are connected but in the wrong order. The lights will illuminate sequentially on both units, but in a different order on the remote side. For example, the main unit may show a 1-2-3-4 sequence while the remote shows 1-4-3-2. This pattern helps you identify swapped wires. It also confirms if you have successfully created a crossover cable, where certain pairs are intentionally swapped.
Advanced Features and Common Troubleshooting Scenarios
While basic testers are great for continuity checks, professional testers offer advanced diagnostics to pinpoint subtle issues that degrade network performance. For complex scenarios, our team at AccuTech Communications offers expert Structured Cabling Services.
How to use an RJ45 network cable tester for advanced diagnostics
Advanced testers provide a deeper look into your network’s health:
- Length Measurement (TDR): Time Domain Reflectometry measures the cable’s length and can even report the exact distance to a fault like a break or short.
- Tone Generator: This “fox and hound” system sends an audible tone down a cable, allowing you to trace and identify it in a bundle with a probe. See how a tone generator works.
- PoE Testing: Verifies the presence of Power over Ethernet (PoE) and measures the voltage and power (watts) being delivered, which is critical for devices like IP cameras and access points.
- Port Flash Function: Makes the corresponding port light on a network switch blink, instantly identifying which port your cable is connected to.
- Link Speed Verification: Confirms the actual speed (e.g., 100 Mbps, 1 Gbps) and duplex settings your cable is achieving with connected network devices.
| Feature | Basic Tester Capabilities | Advanced Tester Capabilities |
|---|---|---|
| Fault Detection | Opens, Shorts, Miswires, Crossovers (via LED patterns) | All basic faults, plus split pairs, impedance issues, crosstalk, attenuation, return loss |
| Length Measurement | None or very rough estimate | Precise length measurement (using TDR), distance to fault |
| Cable Tracing | None | Tone generation (with a probe) for locating cables, Port Flash (to blink switch port light) |
| PoE Testing | None | Detects PoE presence, measures voltage and actual power (watts) delivered |
| Network Connectivity | None | Link speed verification (10/100/1000 Mbps), ping testing, DHCP/DNS validation, network findy |
| Data Performance | None | Qualification (actual data transmission testing), Certification (pass/fail to industry standards) |
How to use an RJ45 network cable tester to solve common issues
Learning how to use an RJ45 network cable tester with these features helps solve tough problems:
- Troubleshooting Slow Network Speeds: If a basic test passes but speeds are slow, an advanced qualification tester can detect subtle issues like crosstalk or attenuation that are bottlenecking your network.
- Locating a Specific Cable in a Bundle: A tone generator and probe make it easy to accurately trace and identify a single cable in a tangled mess.
- Verifying a New Installation: For new business installations, advanced validation or qualification ensures every cable not only connects but also performs to the required standard, preventing future issues.
- Diagnosing an Intermittent Connection: For connections that randomly drop, some advanced testers can run “soak tests” over extended periods to catch sporadic issues or noise events.
Safety Precautions and Proper Storage
Proper care for your RJ45 network cable tester will ensure it serves you reliably for years. Following a few safety and storage rules is key.
Cautions to Observe During Use
Knowing how to use rj45 network cable tester safely is as important as knowing how to read the results. Always follow these rules:
- Never Test Live Circuits: This is the most important rule. Always disconnect the cable from active network devices (routers, switches, PCs) at both ends before testing. Connecting to a live circuit can damage the tester and your network equipment.
- Avoid High-Current Cables: Network testers are for low-voltage data cables only. Do not use them on cables you suspect may be carrying strong electrical currents.
- Use Trusted Testers: Use quality testers from reputable brands to ensure accurate, safe testing.
- Handle with Care: Avoid dropping the tester or exposing it to liquids or extreme temperatures.
Concluding the Test and Storing Your Equipment
After testing, a proper wrap-up keeps your tool ready for the next job:
- Power Off: Turn the tester off to conserve battery life.
- Disconnect Cable: Gently remove the cable from the tester’s ports.
- Store Properly: Keep the tester, its remote unit, and any accessories in its protective case to shield it from dust and damage.
- Keep Clean and Dry: Wipe the tester with a soft, dry cloth and ensure it is stored in a dry place.
Frequently Asked Questions about Using RJ45 Testers
Here are answers to the most common questions people have when learning how to use rj45 network cable tester.
Can a cable pass a test but still not work?
Yes, this can be frustratingly true. A basic continuity test (validation) confirms that wires are connected end-to-end, but it doesn’t measure performance. High-speed networks can be affected by issues that basic testers can’t see, such as:
- Crosstalk: Signal interference between wire pairs.
- Attenuation: The signal weakening over the length of the cable.
- Return Loss: Signals reflecting back toward the source.
- Split Pairs: A subtle wiring error where pairs are mismatched.
These issues can cause slow speeds or connection drops even on a cable that passes a simple test. A more advanced qualification or certification test is needed to detect these performance-killing problems.
What does it mean if the ‘G’ (Ground) light doesn’t turn on?
This depends on the cable type:
- For unshielded (UTP) cables: This is normal. Unshielded cables don’t have a ground shield, so there is nothing for the ‘G’ light to test.
- For shielded (STP/FTP) cables: The ‘G’ light should illuminate. If it doesn’t, it means there is a break in the shield’s continuity. The cable may still pass data, but it has lost its protection against electromagnetic interference.
Do I need a tester if I just made one cable for my home?
While you can skip it, I always recommend using a tester, even for a single cable. It’s a quick and inexpensive way to get peace of mind. A tester eliminates the guesswork of whether you crimped all 8 wires correctly and in the right order. It saves you from hours of future frustration trying to troubleshoot a mysterious network problem that was caused by a faulty homemade cable. Even professionals test every cable they make.
Conclusion
Mastering how to use rj45 network cable tester is a game-changing skill for anyone managing a network. It empowers you to take control of your network’s health by providing immediate, clear feedback on your cabling. You can quickly pinpoint common issues like opens, shorts, and miswires, preventing frustrating downtime and ensuring reliable data transmission.
While basic testers are excellent for continuity checks, advanced features like length measurement, tone generators, and PoE testing can help solve even trickier scenarios. For complex installations or when you need the peace of mind of certified performance, professional services are the best choice.
At AccuTech Communications, we understand that a reliable network is the backbone of your business. Since 1993, we’ve provided certified, high-quality service to businesses in Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Rhode Island. AccuTech Communications provides expert Network Cabling Installation Services to guarantee your network’s reliability and performance.

