Network Cable Showdown: Top Choices in 2024
Network cable plays a crucial role in efficient data transmission and seamless connectivity within any organization. At its core, this essential technology ensures that data flows steadily and securely between computers, servers, and network devices. Whether you’re considering Ethernet cables or exploring the role of RJ45 connectors, understanding the basics can improve the performance of your communication systems. Here’s a quick snapshot:
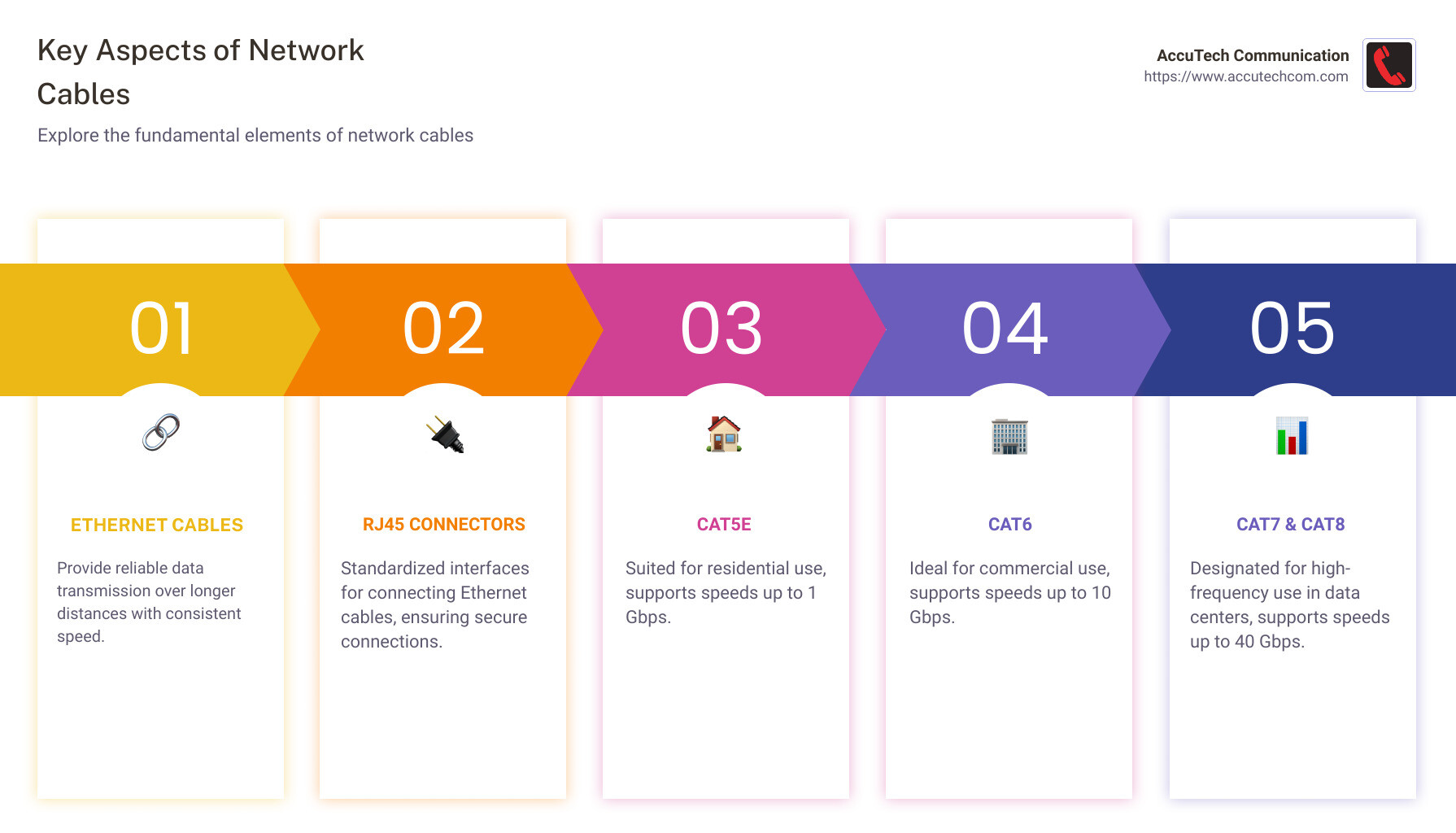
Key Aspects of Network Cable:
- Ethernet cables: Provide reliable data transmission over longer distances with consistent speed.
- RJ45 connectors: Standardized interfaces used to connect Ethernet cables, ensuring secure and reliable connections.
- Different types: Choices include Cat5e, Cat6, and beyond, each suited to different speed and bandwidth needs.
I’m Corin Dolan, owner of AccuTech Communications, with over two decades of experience enhancing business communications across various industries. My expertise lies in helping organizations optimize their network cable infrastructures to meet their specific needs.
Key terms for network cable:
– Types of network wiring
– ethernet cable wiring
– network cable categories
Understanding Network Cables
When it comes to network cables, there are three main types you need to know about: coaxial, fiber optics, and twisted pair. Each type has its unique features and applications, making them suitable for different networking needs.
Coaxial Cables
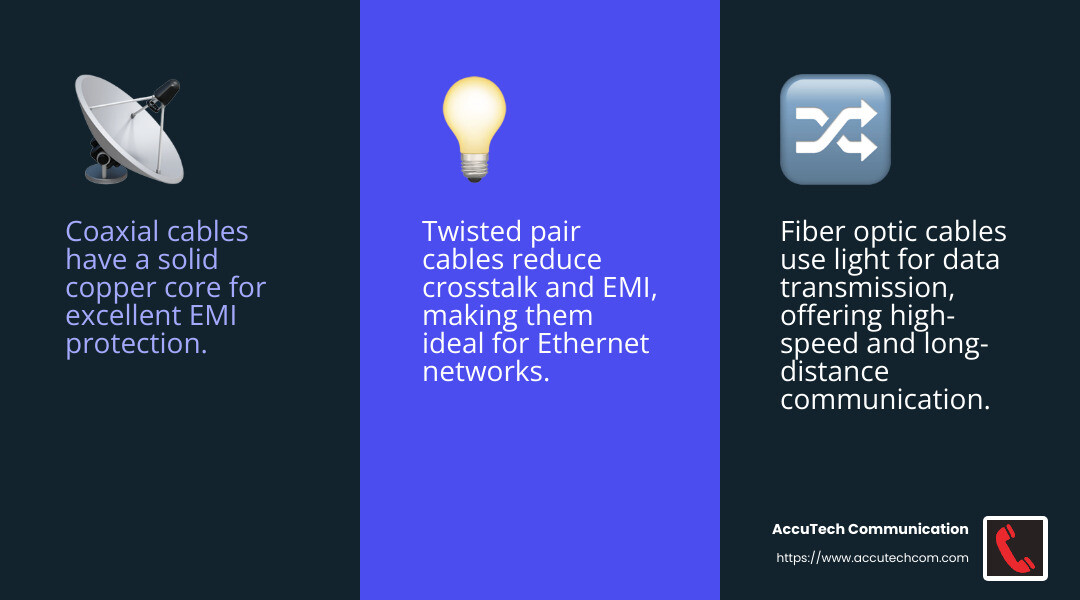
Coaxial cables are one of the oldest types of network cables, originally used in the mid-19th century for undersea cabling. They have a solid copper core surrounded by a conductive shielding layer, which helps prevent electromagnetic interference (EMI). This makes them ideal for environments with high electrical noise.
Coaxial cables are commonly used in broadband internet, television, and radio connections. Their ability to transmit data over long distances without significant loss makes them a reliable choice for certain applications.
Fiber Optic Cables
Fiber optic cables are the go-to for high-speed data transmission. Unlike coaxial cables, fiber optics use light to transmit data, allowing for incredibly fast speeds and long-distance communication. This makes them perfect for data centers and backbone networks where speed and bandwidth are critical.
The use of light instead of electrical signals means fiber optic cables are immune to EMI, providing a clear advantage in environments with high interference. They are also more secure, as tapping into a fiber optic cable without detection is extremely difficult.
Twisted Pair Cables
Twisted pair cables are the most common type of network cable used today, especially in Ethernet networks. They consist of pairs of insulated copper wires twisted together, which helps reduce crosstalk and EMI.
There are two main types of twisted pair cables: Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) and Shielded Twisted Pair (STP). UTP cables are more affordable and easier to install, making them popular in residential and small business networks. STP cables, on the other hand, offer additional shielding for protection against interference, making them suitable for industrial and commercial environments.
Twisted pair cables come in various categories, such as Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat6a, each supporting different data rates and bandwidths. Understanding the differences between these categories can help you choose the right cable for your specific network needs.
In the next section, we’ll dive deeper into Ethernet cables and explore how they form the backbone of modern networks.
Ethernet Cables: The Backbone of Modern Networks
Ethernet cables are the unsung heroes of our digital world. They form the backbone of most Local Area Networks (LANs), providing the essential pathways for data to travel between devices.
Cat5 and Cat5e
Cat5 cables were once the standard for Ethernet networks. They support data rates up to 100 Mbps, which was more than enough for early residential use. However, as internet speeds increased, so did the need for faster cables.
Enter Cat5e (the “e” stands for “improved”). Cat5e cables improved on their predecessor by supporting data rates up to 1 Gbps. This makes them ideal for many home networks today. They offer a good balance of performance and cost, especially for those with internet speeds that don’t exceed 1 Gbps.
Cat6 and Cat6a
For those needing more speed, Cat6 cables are the next step up. They support data rates up to 10 Gbps over short distances (up to 37 meters). This makes them perfect for commercial use, where high-speed data transfer is a must.
Cat6a cables take it even further. They maintain 10 Gbps speeds over longer distances (up to 100 meters). Plus, they come with improved shielding to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI), ensuring a more reliable connection in busy environments.
Cat7 and Cat8
As we move into more specialized territory, we find Cat7 and Cat8 cables. These are designed for high-frequency applications and data centers where top speeds are crucial.
Cat7 cables support speeds up to 10 Gbps over 100 meters, with improved shielding to prevent crosstalk and EMI. They are ideal for high-performance networking in commercial buildings.
Cat8 cables are the latest in Ethernet technology. They can handle up to 40 Gbps, making them suitable for data centers and server rooms where rapid data transfer is essential. With their robust shielding, Cat8 cables are built to operate at high frequencies, offering unparalleled performance.

In the next section, we’ll explore the role of RJ45 connectors in Ethernet networks and how they ensure seamless connectivity.
RJ45 Connectors: The Standard for Ethernet Cables
When it comes to connecting Ethernet cables, RJ45 connectors are the go-to choice. These connectors are crucial for linking devices in networks, ensuring data flows smoothly from one point to another.
Types of RJ45 Connectors
RJ45 connectors are part of the 8p8c (Eight Position, Eight Contact) family, which refers to the eight pins inside the connector. These pins are responsible for transmitting data and power. The RJ45 is the most common example of an 8p8c connector and is specifically designed for Ethernet cables.
There are two main wiring standards for RJ45 connectors: T568A and T568B. The difference lies in the pin configuration for the green and orange wire pairs. While either can be used, have the same standard at both ends of the cable for a straight-through connection. If one end is T568A and the other is T568B, you have a crossover cable, which was traditionally used to connect similar devices directly.
Molded connectors and snagless connectors are variations of RJ45 connectors that add durability and convenience. Molded connectors are permanently attached to the cable, providing a solid, reliable connection that can withstand frequent use. Snagless connectors, on the other hand, have a boot that protects the connector’s locking tab from snapping off, making them ideal for environments where cables are frequently plugged and unplugged.
RJ45 vs Other Connectors
While RJ45 is the standard for Ethernet cables, there are other connectors used in various applications. For instance, RJ11 connectors are typically used for telephone connections and are smaller, with only four or six positions.
In more advanced networking, we encounter connectors like GG45 and ARJ45, which are used with Cat7 cables. These connectors offer backward compatibility with RJ45 while supporting higher frequencies and data rates.
For industrial applications, M12 coded connectors are used. These are designed to withstand harsh environments, offering a waterproof and secure connection, essential for settings exposed to vibrations, extreme temperatures, and moisture.
In the next section, we’ll help you choose the right network cable for your specific needs, considering factors like speed, shielding, and installation location.
Choosing the Right Network Cable for Your Needs
Selecting the perfect network cable can seem daunting, but it boils down to a few key factors: speed, shielding, and installation requirements. Let’s break down what you need to know.
Speed and Data Rate
One of the first things to consider is the data rate of the network cable. This refers to how much data can be transmitted per second, typically measured in Mbps (Megabits per second) or Gbps (Gigabits per second). For basic home use, a Cat5e cable, which supports speeds up to 1 Gbps, usually suffices. However, if you’re running a business or have high data demands, you might opt for Cat6 or Cat6a cables, which offer up to 10 Gbps. For even higher demands, Cat7 and Cat8 cables can handle up to 40 Gbps, making them ideal for data centers and high-frequency applications.
Shielding and Interference
Shielding is crucial in environments with a lot of electromagnetic interference (EMI) or radio frequency interference (RFI). Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) cables, like most Cat5e and Cat6, are fine for low-interference environments. However, if you’re dealing with high EMI, consider Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) cables. These come with various shielding options, such as foil or braided wire, to protect the data signal. Shielding not only prevents external interference but also minimizes crosstalk between the cable pairs themselves.
Cable Length and Installation
When planning your network, consider the cable length. Ethernet cables have a maximum effective length of about 295 feet (90 meters). Beyond this, you might experience attenuation, which is a weakening of the signal. For longer runs, higher quality cables with thicker conductors or additional shielding might be necessary to prevent signal degradation.
Installation location is another factor. If you’re running cables through walls or between floors, look for cables with CMR (riser-rated) or CMP (plenum-rated) jackets. These ratings indicate that the cable jacket meets specific fire safety standards, essential for building safety.
Choosing the right network cable doesn’t have to be complicated. By focusing on these key aspects—speed, shielding, and installation—you can ensure your network is both efficient and reliable.
In the next section, we’ll answer some frequently asked questions to help you further understand the nuances of network cables.
Frequently Asked Questions about Network Cables
What is a Network Cable?
A network cable is a hardware component that connects and transfers data between computers, routers, switches, and other devices within a network. Think of it as the highway for your data, ensuring smooth and efficient data transmission. Network cables are essential for establishing wired connections, which are often more reliable and faster than wireless options.
Is a Network Cable the Same as an Ethernet Cable?
Yes, an Ethernet cable is a type of network cable specifically used for wired networks, like those in homes and offices. While all Ethernet cables are network cables, not all network cables are Ethernet cables. Ethernet cables are designed to handle specific data transmission standards and are categorized by speed and bandwidth, such as Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat6a.
What Cable is Best for Home Network?
Choosing the right cable for your home network depends on your internet speed and future needs.
- Cat5e cables are a great starting point for most homes, offering speeds up to 1 Gbps. They are cost-effective and sufficient for streaming, gaming, and everyday browsing.
- If you anticipate higher data demands or want to future-proof your setup, Cat6 cables provide up to 10 Gbps and better performance over longer distances.
- For those with even greater needs, such as running a smart home or a mini data center, Cat6a cables offer improved speed and shielding, ensuring top-notch performance.
The choice of cable can significantly impact your network’s speed and reliability, so consider your current setup and future plans when selecting a network cable.
Conclusion
At AccuTech Communications, we understand that choosing the right network cable is crucial for the efficiency and reliability of your business communications. Since 1993, we’ve been committed to providing top-notch network cabling solutions across Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Rhode Island. Our certified services ensure that your network infrastructure is optimized for peak performance, whether you’re a small business or a large corporate campus.
Our competitive pricing sets us apart, making high-quality network solutions accessible without breaking the bank. We offer a comprehensive range of services, from structured cabling and fiber optic installations to wireless networking solutions. Our team of skilled technicians and engineers is dedicated to maintaining the highest standards of quality and reliability.
At AccuTech, our commitment to quality means you can trust us to deliver network cabling that stands the test of time. We focus on building lasting relationships with our clients, many of whom have relied on us for over two decades. Your network is the backbone of your business; let us help you make it stronger.
For more information on how we can assist with your network cabling needs, visit our Network Cable Services page.

